Key Takeaways
- The classic 3-2-1 rule keeps three copies on two media with one off-site, yet it now needs to be upgraded for modern threats.
- Veeam’s 3-2-1-1-0 rule adds one immutable copy and verifies zero recovery errors, delivering stronger ransomware resilience.
- Cloud backups, DRaaS, and SureBackup testing simplify administration, maintain compliance, and ensure that data can always be restored.
In the realm of data protection and Veeam, the 3-2-1 Rule has long served as a foundational guideline. This rule outlines the importance of maintaining multiple copies of your data, but as technology continues to evolve, the notion of data redundancy has taken on new dimensions, particularly with the introduction of cloud-based solutions. In this article, we’ll explore how you can enhance your data backup strategy with it.
How does the 3-2-1 Rule Work?
The 3-2-1 rule is a foundational data protection strategy designed to reduce risk and improve recoverability. It recommends that you:
- Maintain three copies of your data: This includes the original data plus at least two copies. This ensures redundancy in case one or two copies are corrupted or compromised during a ransomware attack or a hardware failure.
- Use two different types of media for storage: Store your data on two distinct forms of media, such as local storage and cloud, disk and tape. This diversity helps protect against simultaneous failure of a single media type.
- Keep at least one copy off-site: To further ensure data safety, add a geographic and network separation. Whether it’s a public cloud, a remote data center, or an air-gapped vault, the goal is to isolate backup data from any single point of failure or breach within your primary environment.
This rule works because it embraces redundancy, diversity, and isolation—three principles that underpin disaster recovery, cybersecurity readiness, and compliance. By distributing backups across multiple media types and physical or logical locations, organizations significantly reduce the likelihood of catastrophic data loss.
Is the 3-2-1 Backup Strategy Still Effective Nowadays?
Yes, but only if applied thoughtfully and enhanced for today’s threat landscape. The original 3-2-1 rule wasn’t designed with ransomware, immutable storage, or public cloud in mind. It was developed in a time when tape libraries and physical media dominated backup workflows.
Modern infrastructures now demand more resilient approaches. That’s why the rule remains relevant but no longer sufficient on its own. In today’s environments, a 3-2-1 strategy without immutability or recovery verification creates blind spots that attackers and failure events can exploit. Also, what makes the framework powerful is its adaptability. It’s vendor-agnostic, doesn’t require specific hardware, and can be tailored to nearly any environment. For modern IT, it’s a foundation to build on.
Important Backup Considerations That Strengthen 3-2-1
To apply the 3-2-1 rule effectively today, it’s essential to consider how evolving technologies and threats change your risk profile:
- Deduplication helps reduce backup storage costs but can slow recovery if overused. Balance space savings with performance.
- Cloud storage provides scalable, off-site protection, but comes with cost, bandwidth, and recovery speed considerations. Redundancy across providers can improve resilience.
- Legacy media like tape may still have a role, but maintaining aging libraries is expensive and inefficient. Object storage offers more scalable, long-term archiving options.
- Disaster Recovery as a Service (DRaaS) builds on the 3-2-1 rule by extending protection beyond data to full system and application recovery, which minimizes downtime and business disruption.
Can Cloud Backups Be Used with the 3-2-1 Rule?
In the past, relying on physical media such as tapes and hard drives was the norm. Today, we can achieve rapid recovery, geographic redundancy, and operational simplicity through cloud backups.
Cloud backups not only simplify and modernize data protection but also open new avenues for data security and resilience, ultimately safeguarding your critical information in an ever-evolving digital landscape.
Cloud backups provide several benefits, including:
- Instant Availability: With cloud backups, your data is not only offsite but instantly available, reducing recovery time. There’s no longer a need for the manual process of transferring, cataloging, and tracking physical tapes.
- Data Redundancy: Cloud-to-cloud storage ensures that your backups are stored securely on robust cloud infrastructure, reducing the risk of data loss due to hardware failures or other disasters. Leading cloud providers offer multiple availability zones, guaranteeing uninterrupted data access even if one data center experiences downtime.
- Streamlined Management: Backups can be automated, verified, and tiered for cost control, all while aligning with compliance and retention policies.
- Built-in Immutability: With the help of native APIs such as the Amazon S3 Object Lock API and Immutable Storage for Azure Blob, you can further enhance data security by making your backups immutable and placing them in a WORM (Write Once, Read Many) state. This level of immutability is crucial for maintaining data integrity, ensuring compliance, and safeguarding against potential data breaches.
You can define immutability periods in alignment with your data retention policies, achieving and sustaining the highest standards of security and compliance without incurring unnecessary costs. In essence, these immutability features fortify your data against tampering or accidental alterations, making it an essential component of your comprehensive data protection strategy.
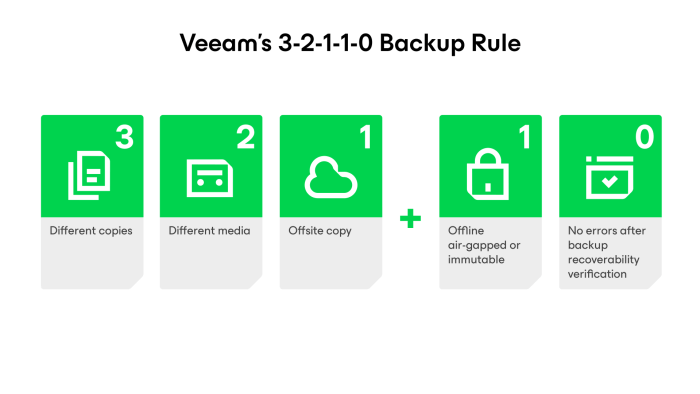
Veeam’s 3-2-1-1-0 Rule for More Secure Backups
At Veeam, we extended the rule to 3-2-1-1-0. It adds one immutable copy, and results in zero recovery errors. This enhanced approach provides a strong foundation for modern data protection and business continuity, fully supported by the Veeam Data Platform.
An immutable or air-gapped copy is essential in modern environments because ransomware increasingly targets backups. If your only protection is connected to your network, it can be compromised. By ensuring at least one copy is unreachable or unchangeable, recovery remains possible even in the worst-case scenario.
The final component, zero recovery errors, is about trust. A backup only matters if you can count on it to restore when it’s needed. Veeam’s SureBackup technology automates recovery verification to confirm that backups are complete, bootable, and ready to restore.
Veeam supports a wide range of configurations that align with the 3-2-1 Rule. The examples below highlight just a few ways this flexibility can be applied to meet the guideline.
- Backups in cloud storage via Veeam Data Cloud Vault, purpose-built for Veeam Data Platform backups
- Backups on disk (DAS, SAN, NAS, and appliances)
- Backups on tape
- Backups on removable storage
- Storage snapshots (caution on separate media from production)
- Backups in object storage such as in the public cloud with the Scale-out Backup Repository’s capacity tier
- Backups in cold archive storage in the public cloud with the Scale-out Backup Repository’s archive tier
- Backups hosted or managed by a service provider, including Veeam Cloud Connect
- Replication to another host or site with Veeam replication
- Backup copy jobs to another storage location
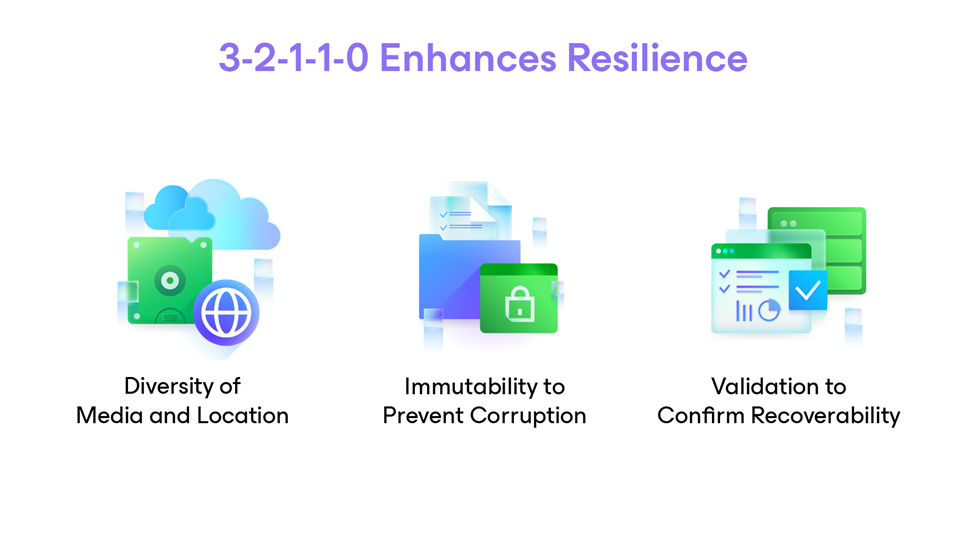
The Veeam difference lies in extending the rule with an extra 1 and 0 which adds immutability and verified recoverability to help ensure recovery across a wide range of incidents. This enhanced rule offers added versatility and peace of mind by going the extra mile.
Looking for Ways to Integrate 3-2-1-1-0 Rule?
As we see, backing up your data is not enough. You must ensure that each backup is recoverable, complete, and uncorrupted. Recovery testing is critical because it ensures that you really are protected against disasters and ransomware attacks. SureBackup recovery verification by Veeam is a great way to confidently know that you can restore data. This isn’t because a Veeam backup isn’t “good” it is just that certain behaviors are only manifested on restores or reboots that may inhibit a restore going as planned.
Veeam Data Cloud Vault, Veeam’s data storage solution, helps ensure your backup strategy aligns with the 3-2-1-1-0 rule by offering strong resilience against cyberthreats while eliminating management complexity and unpredictable costs. It provides an offsite, always air-gapped, encrypted, and immutable copy of your data, fully integrated with the Veeam Data Platform. Keep it in mind for your next refresh!
Leveraging multiple technologies (on-premises repositories, cloud repositories, Veeam Data Cloud Vault, etc.) also proves advantageous in situations where data portability is crucial, such as the need to restore backups from one location to another due to supply chain issues. Veeam not only supports this functionality but also increases your likelihood of achieving successful data recovery when multiple vendors are involved.
Is it Time to Update Your Backup Strategy?
If your organization doesn’t have a structured backup strategy or is still relying on a basic 3-2-1 model, it’s time to reassess. Implementing 3-2-1-1-0 doesn’t require a full rebuild of your infrastructure. It means refining your processes and plugging the gaps that modern threats exploit.
Veeam helps you do this with a platform that is purpose-built for data resilience, cyber recovery, and cross-platform flexibility. Whether you’re modernizing from tape, scaling into the cloud, or building out DRaaS capabilities, we meet you where you are, and help you protect where you’re going. We have nothing but evidence in the form of customer stories at the Veeam website that bad things happen to good servers, storage, and data. Now, more than ever, you need to be able to have control over your data to ensure recoverability. Ready to evolve your 3-2-1 strategy? Let Veeam be your guide. Explore our Cloud Backup Solutions and discover how we can help you achieve data resilience in the modern era.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Is the 3-2-1 backup rule still relevant today?
Yes. Originating in the early 2000s, the 3-2-1 rule is still a foundational data protection strategy because it balances simplicity and resilience. It protects against hardware failure, ransomware, and disasters by having multiple copies across varied locations and media.
2. What is the modern version of 3-2-1 backup?
The modernized framework is the 3-2-1-1-0 rule, which adds two critical layers:
- One more copy stored in an immutable or air-gapped location.
- A requirement for zero backup errors through automated integrity checks and regular restore testing.
3. Can I use only cloud storage for the two-media requirement?
Yes, as long as they are stored on different devices and not identical cloud services. For example, one copy on AWS S3 and another on Azure Blob. But mixing on-prem disk and cloud still offers stronger media diversity.
4. How does 3-2-1 backup rule protect against ransomware?
Having separate backups across different media and locations (with one immutable or off-site copy) protects from encryption and data loss. An immutable replica acts as a trusted recovery source, even when active copies are compromised by a ransomware attack.
