- Veeam Support Knowledge Base
- Job Fails to Start Due to Timeout Caused by Desktop Heap Allocation Failure
Job Fails to Start Due to Timeout Caused by Desktop Heap Allocation Failure
Cheers for trusting us with the spot in your mailbox!
Now you’re less likely to miss what’s been brewing in our knowledge base with this weekly digest
Oops! Something went wrong.
Please, try again later.
The timeout error displayed in Veeam Backup & Replication can be caused by various factors. This article explicitly addresses a scenario where the Windows OS experiences a 'heap allocation' failure.
Please note that the solution provided in this article is only applicable if you have identified Event ID #243 in the Windows System Event Logs (eventvwr.msc). If this event is not present, this article may not provide a relevant solution.
Challenge
In Veeam Backup & Replication, if more than 100 jobs are running simultaneously, and the user attempts to start more jobs, they may fail to start with the following error message:
Error Job <JobName> cannot be started. SessionId: <UUID>, Timeout: [361 sec]
A Veeam Agent for Microsoft Windows backup job may fail with:
Managed session <UUID> has failed
In the Veeam Agent for Microsoft Windows service logs (Svc.VeeamEndpointBackup.log) following errors are found:
Error Job <JobName> cannot be started. SessionId: <UUID>, Timeout: [361 sec] Error Job [Infrastructure update] has failed to start. Timeout expired (6 minutes). SessionId: <UUID>
The following event is found in the System event logs:
Log Name: System Source: Win32k Event ID: 243 Task Category: None Level: Warning Keywords: Classic User: N/A Computer: Description: A desktop heap allocation failed.
Cause
NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM context. If the Windows OS is running out of Desktop Heap memory, new processes can't be started.
Solution
The Desktop Heap size must be increased via a registry modification.
Because this change will affect the desktop heap of all services (also known as non-interactive window stations), do not make the new value larger than necessary.
- Open Registry Editor (regedit) and navigate to
HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Session Manager\SubSystems - Within the SubSystems key will be a Value named Windows.
- Double-click on the value named Windows.
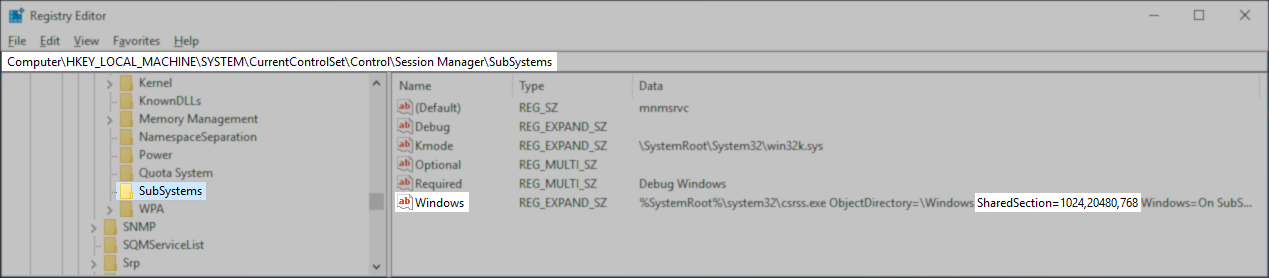
- Find the part labeled "SharedSection=" followed by three values separated by commas.
The third SharedSection value is the desktop heap size for each desktop associated with a non-interactive window station. The value is in kilobytes (KB). - Modify the third value and change it to 2048.
Do not modify any other values.
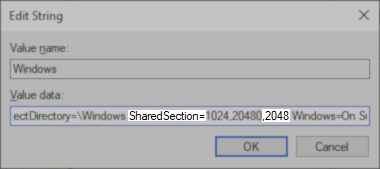
- Click OK to commit the changes.
- Reboot the machine.
More Information
If this KB article did not resolve your issue or you need further assistance with Veeam software, please create a Veeam Support Case.
To submit feedback regarding this article, please click this link: Send Article Feedback
To report a typo on this page, highlight the typo with your mouse and press CTRL + Enter.
Spelling error in text
Thank you!
Your feedback has been received and will be reviewed.
Oops! Something went wrong.
Please, try again later.
You have selected too large block!
Please try select less.
KB Feedback/Suggestion
This form is only for KB Feedback/Suggestions, if you need help with the software open a support case
Thank you!
Your feedback has been received and will be reviewed.
Oops! Something went wrong.
Please, try again later.