TL;DR
When downtime strikes, how fast you can restore your Oracle database?
Veeam Data Platform provides multiple ways to recover your Oracle workloads, from granular RMAN‑based restores to full image‑level recoveries and instant database publishing.With built‑in validation and automation, IT admins and database administrators can restore Oracle 19c, 21c, and 23ai databases confidently across physical, virtual, and cloud environments, all from a single console.
Key Takeaways:
- Restore Oracle databases using RMAN, Veeam Plug‑in for Oracle, or image‑level recovery.
- Validate recovery automatically with integrated verification.
- Test patches and upgrades safely in On‑Demand Sandbox
- Ensure compliance and resilience with consistent restore testing and immutable backups.
Oracle Database underpins many of the world’s most critical applications, from ERP systems to financial services, where even minutes of downtime can significantly impact revenue and reputation.
As hybrid and multi‑cloud infrastructures grow, so does the complexity of reliably protecting and restoring Oracle workloads.
Veeam Data Platform unifies Oracle backup and recovery into one intelligent framework. Whether your database runs on‑premises, in the cloud, or spread across virtual machines (VMs), Veeam simplifies recovery through:
- Native Oracle RMAN integration for command‑line restores managed by database administrators.
- Image‑level recovery for full‑VM or physical‑server restoration.
- Instant Recovery and Veeam Explorer for Oracle for point‑in‑time or transaction‑level restore options.
Veeam allows you to restore Oracle and get your systems back online safely, verifiably, and fast, while meeting even the most demanding RTO and RPO.
Why Reliable Oracle Database Recovery Matters
When an outage or corruption occurs, restoring a database quickly and accurately is what keeps businesses running. Today’s recovery challenges go beyond traditional hardware failure to include:
- Hybrid environments: Oracle workloads now span on‑premises, VMs, and Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) and recovery must be seamless across all of them.
- Ransomware resilience: Modern threats target database backups directly. So, your recovery strategy must include immutable backup repositories and validation to ensure clean restore points.
- Regulatory compliance: Industries under SOX, HIPAA, or GDPR require verifiable recovery testing and documented restore processes.
- Continuous availability expectations: Business units expect RTOs that are measured in minutes, not hours.
Without a tested, automated recovery plan, even the best backup strategy can fail when it matters most.
Oracle Recovery Methods Supported by Veeam Data Platform
Every Oracle environment is different and so are its recovery requirements. That’s why Veeam Data Platform gives database administrators and IT admins multiple ways to restore Oracle databases, depending on how they’re deployed and how much control is needed during recovery.
1. Oracle Database Recovery with Veeam Plug‑in for Oracle RMAN
For database administrators, Veeam Plug‑in for Oracle RMAN fits right into Oracle’s native database recovery tooling.
It registers as an SBT device, so you can run all backup and restore operations straight from the RMAN interface, no extra UI or manual file movement is required.
This example represents a basic same server with a full database recovery as one of the most common operational use cases. Oracle administrators can also use the Plug-in for more advanced scenarios too.
Key benefits:
- Seamless integration with Oracle’s native Recovery Manager (RMAN).
- Restore directly from Veeam repositories or object storage, including OCI Object Storage.
- Support for parallel channels, compression, and catalogue registration to handle large‑scale databases.
- Full database administrator control with the added protection of Veeam’s immutable backup storage.
2. Oracle Database Recovery via Image‑Level Backup
For environments where Oracle runs inside VMs or on physical servers, image‑level backup and restore gives you a fast, reliable way to bring entire systems back online. Veeam captures the full image of the VM or server at the block level by using Change Block Tracking (CBT) to accelerate incremental runs.
During a restore, Veeam automatically handles Oracle’s database state by: placing it in backup mode, taking a snapshot, and releasing it afterward to maintain transactional consistency.
You can then recover:
- The full VM or server for complete restoration.
- Individual disks or files for granular repairs.
- The database itself using Veeam Explorer for Oracle for point‑in‑time or transaction‑level recovery.
3. Oracle Recovery Validation and Testing
A backup isn’t truly reliable until it’s been tested. With Veeam Data Platform, recovery validation is built in. You can automatically verify that a restored Oracle instance boots, mounts, and passes health checks without touching production.
Validation runs through Veeam’s recovery verification workflows, giving teams confidence that their restore points are usable and consistent.
For patch testing or upgrade validation, spin up an isolated environment via On‑Demand Sandbox and run your own scripts before deploying changes to production.
How to Restore an Oracle Database from Backup (Step‑by‑Step)
Restoring an Oracle database from backup is a straightforward process when the recovery method matches your environment and business requirements. With Veeam Data Platform, you can choose the most efficient approach by using native Oracle RMAN, Veeam Plug‑in for Oracle RMAN, or image‑level recovery to meet your recovery time and data‑integrity objectives.
The following step‑by‑step overview outlines how to confidently restore an Oracle database and verify that it is consistent, recoverable, and ready for production.
Step 1: Prepare Your Restore Environment
Confirm that your Veeam Data Platform components and repositories are reachable and that you have the right credentials for your Oracle instance.
If you’re restoring to a different host or test environment, ensure your Oracle home paths and listener configuration matches your production setup.
Step 2: Select the Restore Method
Choose the recovery option that aligns with your deployment and objective:
| Method | Use Case | Restore Scope | Typical RTO |
|---|---|---|---|
| Native Oracle RMAN | Full control from Oracle RMAN interface | Database‑level | Minutes to hours depending on size |
| Image‑Level Restore | VM or physical host recovery | Entire server/VM | Minutes |
| Instant Recovery | Rapid restart of full VM or database | System or application | Under 5 minutes |
| Explorer for Oracle | Point‑in‑time or transaction‑level | Specific database state | Minutes |
Step 3: Initiate the Restore Process
If using RMAN:
Run your restore command within RMAN, targeting the Veeam repository. Example:
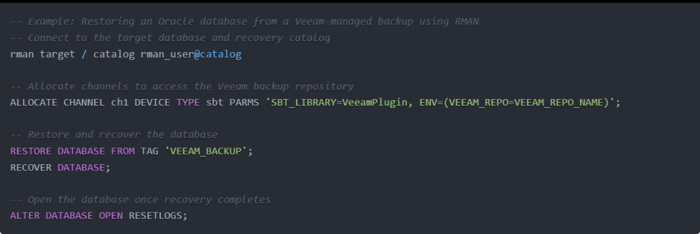
This uses the plug‑in to pull the backup blocks directly from Veeam storage.
If using image‑level restore:
Open Veeam Backup & Replication → select your Oracle VM or server → choose Restore Entire VM or Instant Recovery.
Veeam automatically handles Oracle’s backup mode to keep data consistent.
If using Instant Recovery or Veeam Explorer:
Launch Veeam Explorer for Oracle → pick your restore point → choose restore database, publish database, or point‑in‑time recovery.
Step 4: Validate the Restored Database
After recovery, always verify that the database mounts and opens cleanly.
Use Veeam’s automated recovery verification to confirm that the restored Oracle instance starts without errors.
For deeper testing, deploy an isolated On‑Demand Sandbox and run application queries or scripts before returning the system to production.
Step 5: Document and Confirm Recovery
Record the restore point, method used, and validation results.This documentation supports audit requirements and helps ensure compliance with your organization’s RTO/RPO objectives.
Best Practices for Oracle Database Restore
A successful Oracle database restore means more than data availability. It’s about verified integrity, regulatory compliance, and complete confidence in the recovered environment. The following best practices can help streamline recovery and eliminate uncertainty when every second counts.
| 1. Test your recovery points regularly | Run scheduled restore tests to confirm that backups are usable and consistent. Even a quick verification helps detect corruption or configuration drift before a real event occurs. |
| 2. Validate backups with Veeam verification tools | Use the Veeam’s automated recovery verification to test Oracle restore points. Each verification session powers up the database in an isolated environment, checks startup integrity, and reports the results. |
| 3. Automate restore verification and reporting | Combine verification with scripts or orchestration tools to generate standardized restore reports. Automation not only saves time but also supports audit readiness and regulatory compliance. |
| 4. Separate and protect archive logs | Keep Oracle archive logs on dedicated storage and back them up frequently, typically every 5 to 15 minutes. This enables point‑in‑time recovery and minimizes potential data loss between full backups. |
| 5. Use immutable repositories for ransomware defense | Keep Oracle archive logs on dedicated storage and back them up frequently, typically every 5 to 15 minutes. This enables point‑in‑time recovery and minimizes potential data loss between full backups. |
| 6. Leverage on‑demand sandbox for testing and upgrades | Before upgrading Oracle Database or applying patches, spin up an On‑Demand Sandbox environment. You can safely test changes against a restored copy without impacting production workloads. |
| 7. Document every restore event | Maintain a record of restore operations, including method used, restore point, validation results, and time to completion. This documentation supports internal SLAs and demonstrates compliance during audits. |
Troubleshooting Common Oracle Restore Scenarios
Even with a well‑planned recovery process, Oracle restores can present unexpected challenges. Below are common situations database administrators encounter and how Veeam Data Platform helps resolve them quickly.
What if my archive logs are missing?
Archive logs are essential for point‑in‑time recovery. If they’re unavailable or corrupted, you can still perform a complete database restore from the latest full backup by using Veeam Plug-in for Oracle RMAN or image‑level recovery. After restoration, recreate missing archive logs through Oracle’s recovery commands or roll forward using the most recent transaction data.
Tip: Configure frequent archive‑log backups (every 5 – 15 minutes) and store them in a separate, immutable repository to prevent this issue.
Can I restore to a different Oracle host or test environment?
Yes. Veeam Data Platform supports restores to alternate hosts and sandbox environments.
Simply configure target parameters in the RMAN console or use Instant Recovery to mount the database on a different VM or server. This flexibility is ideal for migration testing, patch validation, or disaster recovery (DR) drills.
How can I verify consistency after restoration?
Verification depends on your deployment configuration. Once the restore completes, use Veeam’s automated recovery verification to confirm that the Oracle instance starts cleanly, mounts properly, and passes health checks. For deeper confirmation, run functional queries or application transactions in an On‑Demand Sandbox to validate business logic before resuming production operations.
Why does my restore take longer than expected?
Recovery time can vary based on:
- Database size and the number of datafiles.
- Network bandwidth between Oracle server and Veeam repository.
- Restore method: RMAN vs. Instant Recovery vs. Image‑level restore.
To optimize performance:
- Use parallel RMAN channels for large databases.
- Verify repository throughput and disk I/O health.
- Schedule restores during off‑peak times if possible.
What if the restored database doesn’t open properly?
If Oracle fails to open after recovery, check alert logs for missing datafiles or redo logs.
Run an RMAN RECOVER DATABASE command to apply any remaining archive logs.
If corruption is suspected, validate backup integrity with Veeam’s verification feature and restore from the last known good recovery point.
Pro tip:
Keep backup job logs and restore reports centralized in Veeam Data Platform’s monitoring console. This console provides immediate insight into what happened during recovery and simplify troubleshooting across hybrid environments.
Conclusion:
With Veeam Data Platform, organizations can unify Oracle backup, replication, and recovery within one intelligent, automated framework. Whether you’re restoring a single transaction or an entire production database, Veeam delivers verified, fast, and compliant recovery every time.
See it in Action
Request a Veeam Data Platform demo and explore how automated recovery verification and instant restore options can simplify Oracle Database protection across hybrid and cloud environments.
FAQs
How do I restore an Oracle database from a Veeam Data Platform backup?
To restore an Oracle database from backup using Veeam Data Platform, select your restore method (Veeam Plug-in for Oracle RMAN, image‑level, or Instant Recovery) then point to your desired restore point. Veeam automates database consistency and uses automated recovery verification to confirm the database starts cleanly before returning it to production.
Does Veeam Data Platform support Oracle RMAN integration?
Yes. Veeam Data Platform includes a certified Veeam Plug‑in for Oracle RMAN that registers as an SBT plug‑in. This allows database administrators to manage backups and restores directly from the RMAN console while storing data in Veeam repositories or cloud object storage.
Can I perform point‑in‑time recovery with Veeam Data Platform?
Yes, you can perform point‑in‑time recovery by combining RMAN backups with Oracle archive logs or by using Veeam Explorer for Oracle to select a specific transaction or timestamp. This enables granular recovery without rolling back the entire database.
What’s the difference between image‑level and RMAN‑based restores?
| Feature | Image‑Level Restore | RMAN‑Based Restore |
|---|---|---|
| Control | Managed through Veeam UI | Controlled via RMAN console |
| Use Case | Full VM / server recovery | Database‑only restore |
| Speed | Faster for system‑level recovery | More granular for data restoration |
| Typical User | IT administrator | Database administrator |
How do I validate Oracle restore consistency automatically?
Use Veeam’s automated recovery verification to confirm every restored Oracle Database instance is bootable and consistent. This process runs post‑restore checks and can be extended with On‑Demand Sandbox testing to validate performance or patch upgrades before returning to production.
