Key Takeaways
- Why Companies are moving Away from VMware
Rising licensing costs, vendor roadmap uncertainty, and complex operations are prompting many organizations to evaluate simpler, more cost‑efficient, and cloud‑aligned alternatives. - Top Factors When Choosing a VMware Alternative
Compare cost models, management simplicity, required skillsets, scalability, and ecosystem integration across options like Hyper‑V, Nutanix AHV, Proxmox VE, KVM distributions, and Scale Computing. - How to Migrate Safely to a New Platform
Follow a structured process. Take inventory of your workloads, validate the target environment, test recovery, pilot migrations, and maintain rollback plans to minimize downtime and data loss. - Best Practices for Long‑Term Resilience
Combine frequent backups, immutable or offsite storage, replication, and automated recovery testing to meet recovery time objective/recovery point objective (RTO/RPO) goals and ensure business continuity across diverse hypervisors.
For years, VMware has been the standard in enterprise virtualization. However, rising licensing costs, roadmap uncertainty, and evolving IT strategies are prompting many organizations to explore new options. Whether driven by budget pressure, a desire for simpler operations, or the need to align with hybrid and multi‑cloud goals, the search for VMware alternatives is accelerating.
In this guide, we’ll compare the top five VMware alternatives: Microsoft Hyper‑V, Nutanix AHV, Proxmox VE, Oracle Linux KVM, and Scale Computing HyperCore. We’ll outline their strengths, trade‑offs, and best‑fit scenarios. You’ll also get a practical decision framework to help you shortlist the right hypervisor for your environment as well as a migration playbook to ensure a smooth, low‑risk transition.
No matter which platform you choose, data protection is critical during and after migration. delivers cross‑platform backup, instant recovery, and orchestrated disaster recovery (DR) for VMware and all major alternatives, which gives you the confidence to migrate without risking prolonged downtime, data loss, or compliance gaps.
Why Organizations Are Evaluating VMware Alternatives
Virtualization has been the backbone of enterprise IT for two decades, but recent changes in the VMware ecosystem are forcing organizations to rethink their strategies. What was once a flexible, predictable platform has become a source of concern for many IT leaders, which has been driving and a new wave of evaluation.
1. Cost and Licensing Pressure
One of the biggest catalysts for change is cost. VMware’s licensing model has shifted toward higher pricing, SKU consolidations, and more rigid contract structures. For organizations with hundreds or thousands of workloads, even small changes in licensing terms can create significant budget challenges.
Many CIOs and IT directors are now under pressure to find a more predictable, cost-efficient virtualization model that won’t escalate unpredictably year-over-year.
2. Vendor and Roadmap Uncertainty
Beyond cost, there’s also the issue of long-term stability. Mergers, acquisitions, and roadmap changes create uncertainty around how VMware will evolve and how those changes will impact customers.
Many IT teams want to reduce platform risk by diversifying or moving to hypervisors that have clearer long-term roadmaps and open ecosystems.
3. Complexity in Operations
VMware remains feature-rich, but some organizations are questioning whether they need that level of complexity. For mid-market enterprises, managed service providers (MSPs), and organizations with lean IT teams, the operational overhead of VMware can feel heavy compared to newer hypervisors that emphasize simplicity, automation, or community-driven support.
4. Skills and Talent Gaps
Another pain point is skill availability open‑source hypervisors such as Proxmox VE or KVM variants may reduce licensing costs, but at scale, they often require deeper expertise and carry added operational complexity due to less polished tooling. Enterprise options like Hyper‑V or Nutanix AHV can tap into existing skills in Windows or converged infrastructures, which minimizes retraining.
5. Desire for Flexibility and Modernization
Many organizations are taking this moment to rethink not just their hypervisor, but their entire IT strategy too. Hybrid and multi-cloud adoption, containerization, and edge computing are expanding the technology stack. Companies are asking:
- Which hypervisors align best with our cloud roadmap?
- How easily can we migrate workloads without lock-in?
- Can we standardize on fewer tools while also preparing for modernization?
This is why VMware alternatives are gaining traction not only as “replacements” but as opportunities to reset for cost efficiency, flexibility, and long-term resilience.
Top VMware Alternatives: Platform Deep Dives
Before choosing a new virtualization platform, it’s important to understand how each option compares in terms of cost, features, scalability, and ecosystem fit. In this section, we break down the strengths and considerations of top VMware alternatives so you can match the right hypervisor to your business needs.
Remember, no matter which platform you select, a is key to ensuring consistent protection, smooth migrations, and long‑term resilience.
Microsoft Hyper-V
Microsoft Hyper-V remains one of the most mature and widely deployed enterprise hypervisors. For organizations already invested in the Microsoft ecosystem, Hyper-V offers a familiar path with seamless integration.
Strengths
- Cost efficiency: Hyper-V is bundled with Windows Server at no additional licensing cost, making it appealing for organizations with existing Microsoft licensing agreements.
- Ecosystem integration: Deep compatibility with Active Directory, System Center, and Azure Arc for hybrid management.
- Scalability: Supports large clusters, live migration, and advanced features like Storage Spaces Direct.
- Talent availability: Many IT teams already have Windows expertise, which reduces training overhead.
Considerations
- Feature parity with VMware: While strong, certain advanced VMware features (e.g., vSAN-level storage integrations) may not have direct equivalents.
- Licensing complexity: Savings depend on how Windows Server and client access licenses (CALs) are structured in your organization.
- SCVMM licensing costs: Larger environments that require a single management plane should factor in the additional cost of System Center Virtual Machine Manager licensing.
- Hybrid model: Best suited for organizations that are already aligned with Microsoft’s cloud and licensing ecosystem.
Nutanix AHV
Nutanix AHV is a hypervisor that’s tightly integrated into Nutanix Cloud Platform and designed for simplicity and hyperconverged infrastructure (HCI). It’s a common choice for customers who are modernizing their datacenters.
Strengths
- Integrated platform: AHV is included at no extra cost with Nutanix Cloud Platform, which reduces hypervisor spend.
- Simplicity: Streamlined management through Prism, with strong automation and monitoring built in.
- Resiliency: Features like native replication, snapshots, and DR orchestration aligns well with enterprise requirements.
- Cloud extension: Native tie-ins with Nutanix Cloud Clusters (NC2) for hybrid and multi-cloud strategies.
Considerations
- Vendor lock-in: Requires full adoption of Nutanix HCI stack, not just the hypervisor.
- Ecosystem scope: While growing, AHV doesn’t yet match VMware’s extensive ecosystem of third-party integrations.
- Skillset shift: Teams must learn the Nutanix way of managing infrastructure, which may differ from VMware workflows.
Proxmox VE
Proxmox VE is a popular open-source hypervisor that combines KVM virtualization with container orchestration (LXC). It’s favored by smaller organizations, labs, and MSPs that want flexibility without steep licensing fees.
Strengths
- Cost-effective: Free to use, with an optional subscription for enterprise support.
- Lightweight and flexible: Combines virtualization and containerization all in one platform.
- Community-driven: Strong open-source community with fast innovation and shared best practices.
- Management simplicity: Intuitive web interface, especially for smaller environments.
Considerations
- Enterprise support: Commercial support is available, but it’s not as robust or widespread as VMware or Nutanix.
- Scalability: Works well for small- to medium-sized businesses (SMBs) and MSPs, but very large enterprise deployments may encounter operational limits in areas like centralized management, automation, and high‑volume workload handling.
- Ecosystem maturity: Hardware compatibility lists and integrations aren’t as extensive as proprietary platforms.
Oracle Linux KVM
Oracle Linux KVM is Oracle’s enterprise-ready implementation of the open-source Kernel-based Virtual Machine (KVM) hypervisor. It delivers a secure, stable, and fully supported virtualization platform that’s optimized for Oracle Linux environments. Built on upstream KVM, it provides performance, scalability, and integration with Oracle Cloud Infrastructure, making it ideal for organizations that are standardizing on Oracle technologies.
Strengths
- Open-source flexibility: No vendor lock-in, giving you full control over configuration.
- Enterprise support: Oracle, as well as RHEL-based options, can come with commercial-grade support and ecosystem certifications.
- Performance: KVM is efficient and forms the basis of many public cloud hypervisors, including AWS and Google Cloud.
- Community: Large ecosystem of tools, integrations, and contributors.
Considerations:
- Operational overhead: Running upstream KVM or oVirt requires more Linux expertise than VMware.
- Migration complexity: Workload moves can require careful planning and third-party tools.
- Feature depth: While powerful, some enterprise-grade features (like turn-key DR orchestration) may require bolt-on solutions.
Scale Computing/HyperCore
Scale Computing HyperCore is a hyperconverged virtualization platform that’s designed for simplicity and efficiency, especially in SMBs, edge environments, and distributed enterprises. It integrates compute, storage, and virtualization into a single, easy-to-manage solution.
Strengths
- Simplicity: Streamlined deployment and management, no need for separate hypervisor, storage, or virtualization licensing.
- Edge-ready: Well-suited for remote offices and edge use cases where IT resources are limited.
- Cost-efficient: Offers a lower total cost of ownership compared to VMware.
Considerations
- Ecosystem integrations: While expanding, it does not yet have the same breadth of integrations as more mature platforms.
Oracle Linux KVM (OLVM)
Oracle Linux Virtualization Manager (OLVM) is Oracle’s enterprise-supported KVM virtualization platform that’s built for organizations that are already leveraging the Oracle ecosystem. It offers tight integration with Oracle Linux and related technologies.
Strengths
- Oracle ecosystem alignment: A natural fit for Oracle-heavy environments, with seamless compatibility across Oracle databases and applications.
- Enterprise support: Backed by Oracle’s support services to ensure stability for mission-critical workloads.
- Cost flexibility: Included with Oracle Linux Premier Support, often making it cost-effective for existing Oracle customers.
Considerations
- Adoption scope: Primarily used by Oracle customers; not widely adopted outside that base.
- Ecosystem maturity: Fewer third-party integrations compared to VMware or Hyper-V.
- Complexity: May require specialized Oracle expertise to maximize benefits.
These six platforms reflect the most realistic paths VMware customers are evaluating today, each with unique trade-offs.
How to Choose a VMware Alternative: A Practical Decision Framework
Use this quick framework to narrow options based on what matters most in your estate. Think “pick your top two or three drivers,” then shortlist.
1) Cost and Commercial Model
- Priority: Lower TCO, predictable spending, and avoid per-CPU core surprises.
- Lean toward: Hyper-V (bundled with Windows Server), Proxmox VE/KVM (open source), Nutanix AHV (hypervisor included in HCI subscription).
- Watchouts: Support service level agreements (SLAs), skills required, migration tooling, and any hidden dependency/licensing.
2) Operating Model and Skills
- Priority: Fast ramp for existing teams.
- Lean toward: Hyper-V for Windows-centric operations; Nutanix AHV for simplified HCI with Prism; VMware if you’re staying put short-term while planning a transition.
- Watchouts: Linux/KVM expertise for Proxmox/upstream KVM at scale; new runbooks for Prism/Flow.
3) Application and Platform Fit
- Priority: Microsoft Certified for Hyper-V), drivers, and ecosystem integrations for your stack.
- Lean toward:
- AHV if you’re modernizing to HCI and want integrated data services.
- Hyper-V for Microsoft-heavy stacks and Azure-connected ops.
- KVM/Proxmox for bespoke/Linux-forward environments.
- Watchouts: Special appliances, legacy OSes, and kernel/virtIO driver nuances.
4) Resilience and Orchestration
- Priority: Built-in HA/DR, simple runbooks, and testable failover.
- Lean toward: AHV (Leap), Hyper-V with clustering + orchestration (Veeam Recovery Orchestrator).
- Watchouts: Ensure your DR workflows, runbooks, and recovery SLAs are validated on the target platform, not just backup SLAs.
5) Hybrid/Cloud Strategy
- Priority: Consistent operations across on-premises and the public cloud.
- Lean toward:
- Hyper-V for Azure-aligned operations.
- Nutanix NC2 for consistent Prism across AWS/Azure.
- VMware Cloud Foundation if you’re keeping vSphere semantics during a phased transition.
- Watchouts: Network overlays, identity/role mapping, landing-zone standards, and cost governance.
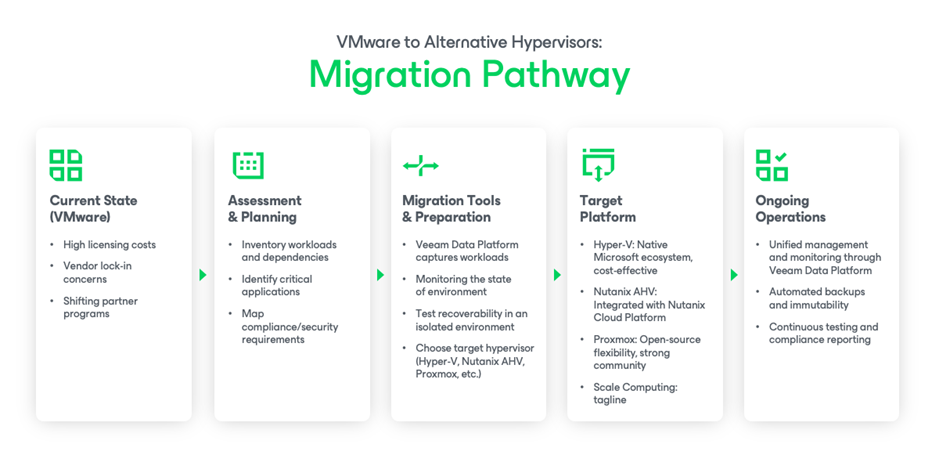
Step-by-Step Migration Playbook: From Shortlist to Cutover
A clean, low-risk migration hinges on inventory, testing, and reversible steps.
| Step 1: Baseline and Prioritize | • Inventory VMs, OS versions, drivers, tools, inter-VM dependencies, and data locality. • Classify workloads (Tier-1/2/3) and define RPO/RTO per tier. • Identify “known tricky” items (e.g., legacy NIC/SCSI drivers, proprietary kernels, appliances). |
| Step 2: Readiness and Target “Hello World” | • Stand up the target platform and validate core services: Storage, networking, identity, monitoring, and backup. • Prove fundamentals with a golden test VM (e.g., I/O, network, snapshots, backup/restore). |
| Step 3: Protect First (Safety Net) | • Ensure backup and recovery are in place for both source and target. • Create immutable copies. |
| Step 4: Pilot Migrations | • Start with low-risk workloads; use V2V tools or clean restores (often the safest). • Validate app behavior, performance, security controls, and operational runbooks (e.g., backup, monitoring, patching). |
| Step 5: DR and Compliance Proving | • Run tabletop and orchestrated failover/failback on the target platform. • Produce audit artifacts (e.g., evidence of test success, RTO/RPO attainment, approvals). |
| Step 6: Phased Cutover with Rollback | • Batch by environment or application domain. • Maintain a rollback plan per wave (e.g., snapshot/restore point and network reversion). • Track issues in a migration runbook and feed lessons into the next wave. |
| Step 7: Decommission and Optimize | • After a stability window, decommission source capacity. • Tune backup policies, right-size instances, and review cost controls. |
Ready to Take the Next Step?
Whether you’re staying with VMware or moving a different hypervisor, Veeam ensures your data is always protected and recoverable.
Explore how Veeam Data Platform delivers cross-platform resilience and risk-free migrations.
