Key Takeaways:
- Ransomware attacks increasingly target backup repositories, making data protection strategies more critical than ever.
- Air gap backups physically or logically isolate data from networks, preventing remote tampering by attackers.
- Immutable backups lock backup data from alteration or deletion for a defined period.
- Air gap backups offer maximum isolation, but recovery can be slower; immutable backups provide faster recovery with continuous accessibility. Combining both methods enhances protection.
- Veeam’s Data Cloud Vault delivers managed, immutable, and logically air gap cloud storage tailored for cyber resilience.
- Regular backup testing, access control (MFA, role separation), and monitoring with Veeam ONE fortify data recovery readiness.
- For full cyber resilience, organizations should also address access reduction, compliance needs, and backup integrity testing.
According to the Risk to Resilience: 2025 Ransomware Trends and Proactive Strategies report, out of the 1,300 ransomware victims surveyed, 89% had their backup repositories targeted. While almost half of the organizations paid ransom, 17% of organizations reported they couldn’t retrieve their data, despite giving in to the attacker’s demands.
With cyberthreats on the rise, it’s not surprising that a lot of companies are adopting immutable and air-gap (i.e., survivable storage) technologies to ensure their data recovery efforts aren’t hindered by ransomware and they can recover their minimum viable business.
This blog explores the differences between air-gap and immutable backup technologies and how organizations can leverage both in their cyber resilience strategy.
Why Air Gap Backups Matter Today
An air-gap backup isolates your critical data by separating it from the network by physically removing the drive, disconnecting the network ports, or using digital methods of blocking network traffic.
The benefits of air-gapping backups include the following:
- Protection against ransomware and other malware. Since these backups aren’t accessible from the backup server or elsewhere on the network, it’s harder for attackers to access or corrupt them. An attacker needs to be physically present and have the proper access credentials to delete the data. If the backups are properly ejected/isolated and cared for (e.g., temperature controlled, dirt/dust, humidity, etc.), the chances of a failed recovery are low.
- Prevention of unauthorized access and data breaches. It’s best practice for air-gap backups to have an extra layer of protection in the form of encryption. This ensures that if an attacker does gain access to your backups, they can’t restore them and view the contents. Compare this to a scenario where you have a local backup of your domain controller without encryption, and a bad actor restores your backup on their server. They can now leisurely farm your credentials to prepare for an attack on your production systems.
Encryption of the backups (especially those off-site) is critical to preventing unauthorized users from accessing the company’s sensitive data.
- Preservation of data integrity. The contents of the backup remain unaltered, providing both accuracy and consistency, which are crucial for regulatory compliance and reliable recovery. For organizations including health care, government, and finance, keeping various types of data long-term can range from years to indefinitely. They also require maintaining a secure chain of custody in some cases. Failure to comply with industry regulations can result in hefty fines and significant damage to your brand.
The Power of Immutable Backups in Modern Cybersecurity
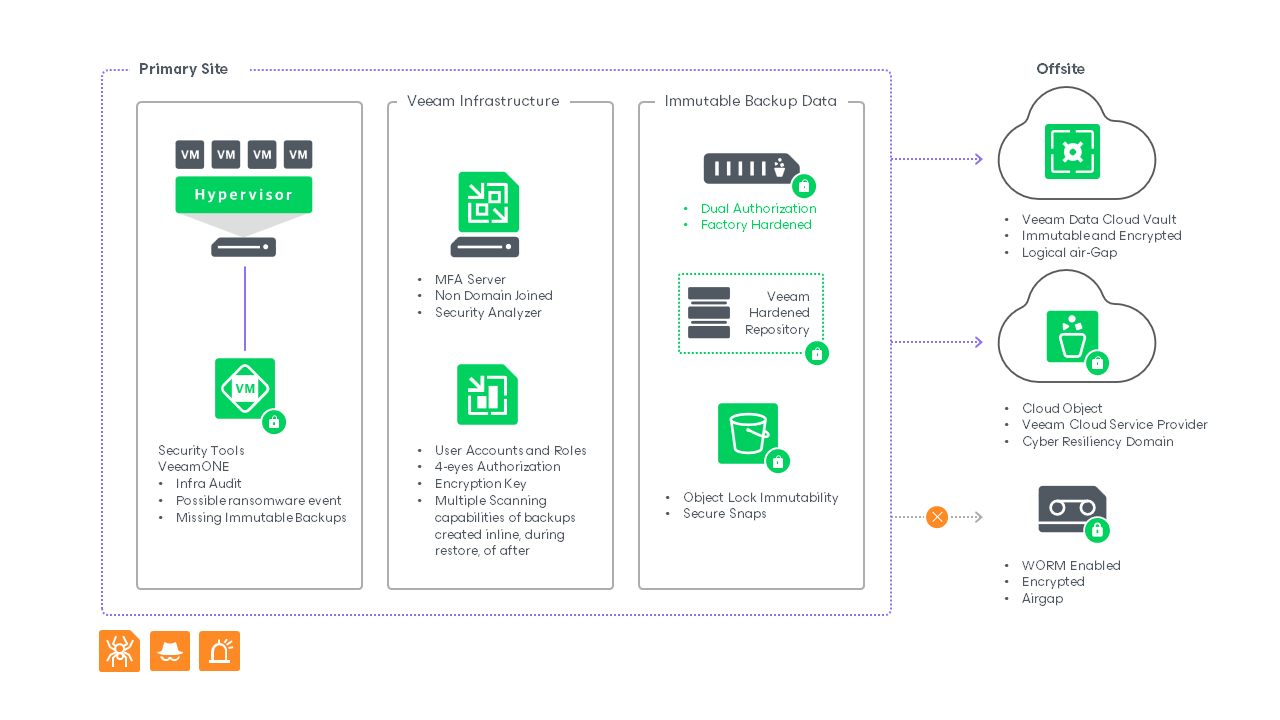
An immutable backup is a copy of data with role-based access controls and other authentications, and it can’t be changed or deleted until a set time has expired. However, it isn’t offline like an air-gap backup, as it’s stored on a device accessible via the internet or network. Multiple technology vendors leverage this type of backups, whether on-premises or in the cloud, in the form of object locks, secure snapshots, and the Hardened Repository from Veeam.
Common Types of Immutability Features and Their Advantages:
| Object Lock (Cloud Storage) |
|
| Secure Snapshots |
|
| Veeam Hardened Repository |
|
| WORM (Write Once, Read Many) Media |
|
Immutability helps protect against ransomware attacks and insider threats, preventing unauthorized parties from altering or encrypting the data in the backups. Even if an attacker gains physical access to an immutable backup, the damage they can do is limited.
Air Gap vs. Immutable Backups: What Are the Key Differences
Air gap and immutable backups both strengthen your cyber resilience, but they aren’t the same. Understanding their distinct capabilities is key to building an effective data protection strategy for your organization.
At a high level, both approaches safeguard data from ransomware, malware, and insider threats, while supporting regulatory compliance. But the way they protect — and how quickly you can recover — differs significantly.
Both types of backup offer resistance against ransomware and data compliance, but that’s where the differences come in.
A traditional air-gap backup, such as tape, can incur an additional cost for managing the media and working with vendors to store it properly. This also holds true for immutable storage because it can grow exponentially if data policies change.
Recovery Time Objectives (RTO) are also a variable depending on the storage media used. For example, a business operating in a remote area with slow network connections or metered data might find recovering data from a cloud backup too slow for its requirements. In this instance, keeping tapes on-site provides a cost-effective and quick way to recover from ransomware attacks. Off-site/cloud backups act as a last line of defense.
| Feature | Air Gap Backup | Immutable Backup |
|---|---|---|
| Access | Completely offline or isolated; no network access | Always online but protected against modifications |
| Modification/Deletion | Physically disconnected and it can’t be accessed remotely | Data cannot be altered or deleted until retention period expires |
| Common Media | Tape, offline drives, disconnected storage | Cloud object storage (S3 Object Lock), Veeam Hardened Repository, Secure Snapshots |
| Cost | Higher operational costs (media handling, vendor storage) | Scales with data growth; typically less operational overhead |
| Recovery Time (RTO) | Longer, especially if media is off-site | Faster recovery; immediate access to backup data |
| Best for | Ultimate isolation, compliance, and long-term retention | Rapid recovery, ransomware defense, and frequent backups |
| Weakness | Physical logistics can slow recovery | Still accessible via network; risk if controls are weak |
At Veeam, we don’t see air-gapped and immutable backups as an either-or decision. They complement each other.
By combining the physical isolation of air gap backups with the fast recovery and tamper-proof protections of immutability, organizations can:
- Strengthen defenses against both cyber and physical threats
- Meet diverse compliance and retention policies
- Reduce downtime while ensuring data integrity
And with solutions like Veeam Data Cloud Vault, customers gain managed cloud storage that’s both immutable and logically air-gapped, offering flexible recovery with robust security with no compromises.
Real-life Example: GORI – Critical Infrastructure Business Challenges
| Company: | Challenge: | Results: |
|---|---|---|
| At GORI, 1,000 employees work every day to distribute water to the 1.5 million citizens living in 75 municipalities between the Italian provinces of Naples and Salerno. | As a provider of critical national infrastructure, GORI must ensure its digital systems are well protected against cyber threats. With ransomware risks, the company aims to strengthen its data protection capabilities by creating immutable, off-site backups. |
|
A European-based water company GORI switched to Veeam as part of a broader plan to strengthen its ability to recover from cyber incidents. GORI had an existing backup strategy but found it was labor-intensive to manage. The company switched to Veeam Data Cloud Vault, a preconfigured and fully managed cloud storage solution. It offers immutable and logically air gap protection for backups.
Veeam Data Cloud enables GORI to recover on-premises systems and Microsoft 365 more quickly than its previous backup solution. It also facilitates regulatory compliance, thanks to its use of the 3-2-1-1-0 backup rule. The company benefits from increased resilience and improved RTOs.
With Veeam, customers can build a data-resilient strategy that works for them. The choice between air-gapping and immutability isn’t an either/or situation. Just as VM replicas aren’t backups and vice versa, air gap backups aren’t necessarily immutable backups. Both technologies exist to help organizations protect and recover data faster. Leveraging them in tandem increases the chance of successful recovery after a cyber event.
What Are the Core Elements of Cyber-Resilient Strategies
Ensuring Survivable Backup Targets
For decades, air gap storage has been a cornerstone of data protection, especially via Write Once, Read Many (WORM) media like tapes or rotating hard drives. Once removed and stored off-site, these backups remain shielded from network-based threats. Today, air gap storage is often complemented by hybrid cloud solutions, though some industries still rely on physical isolation.
- Immutability has gained traction as a modern alternative. It offers WORM-like protection without the physical handling of media, providing locked backups that can’t be changed or deleted for a defined retention period. Unlike air-gaps, immutable backups remain online but are hardened against tampering.
- Building a cyber-resilient strategy requires leveraging both methods where appropriate — combining air gap storage for deep protection with immutable backups for faster recovery options.
- It remains a best practice to follow the 3-2-1 backup rule:
- 3 copies of your data
- 2 types of media
- 1 copy kept off-site
- In typical Veeam deployments:
- Copy 1: Production data (disk)
- Copy 2: Local backup repository (disk)
- Copy 3: Off-site backup (disk, cloud, or tape)
- Many organizations have advanced to the 3-2-1-1-0 rule, adding:
- 1 backup that is either immutable or air-gapped
- 0 errors, verified through testing and validation
- The modern version of having off-site backups often means using cloud storage and storing data in different data centers. This is a particularly useful backup strategy because it protects against local incidents, such as theft or fires, and widespread natural disasters. A flood or earthquake that significantly damages an entire city could wipe out the backups stored at your business premises, but it’s unlikely to impact the copy stored at a Google, Microsoft, or Amazon data center several hundred miles away.
- To support this, Veeam Data Cloud Vault provides cloud storage that aligns with the 3-2-1-1-0 principle. Backups are always stored in a WORM state, encrypted by default, and ready for rapid recovery.
Reducing Access Opportunities
- Start with strong access controls on your production environment. You can use Veeam ONE to monitor the production environment for suspicious activity and run reports to protect your workloads and have encrypted immutable backups.
- Next, define user account roles with proper separation of duties to ensure only relevant individuals can work with your backups. Implement Four Eyes Authorization to ensure key actions require the approval or verification of at least two authorized individuals.
- Enable multifactor authentication (MFA) on your Veeam Backup Server to prevent malicious actors from accessing it, even if an employee’s login credentials are compromised.
- Use an immutable target as your first backup layer. This ensures that even in the event of a bug, ransomware infection, or accidental deletion, you have a reliable recovery point.
- Your third copy of data should remain off-site, encrypted, and ideally offline or air-gapped. This isn’t just for disaster recovery. It also addresses data integrity concerns, legal holds, and compliance with data retention regulations.
For cloud backups, make sure your provider aligns with your industry’s regulatory requirements. Some sectors require compliant, secure cloud services rather than general-purpose public clouds, particularly when it comes to encryption, access control, and audit capabilities.
Regular Testing and Updating
A backup is only as good as your ability to recover it. That’s why it’s critical to keep your backup and recovery software up to date, alongside staying informed on the latest security and disaster recovery trends.
Regularly test your backups and recovery processes. Simulate various disaster scenarios like ransomware attacks, server outages, or hardware failures. Key questions to ask:
- How quickly can you restore operations?
- Do your backups capture all critical data and dependencies for minimum viable business?
Conduct these simulations periodically, not just once. Organizational changes, new systems, or shadow IT practices can lead to data being overlooked in backup plans. For example, employees may use unauthorized tools that aren’t yet included in standard backup configurations.
By validating backups frequently, you ensure your recovery coverage is complete, and you can restore with confidence when an actual incident occurs.
Protect Your Data With Veeam
In the Risk to Resilience Report, 69% of the 1,300 surveyed organizations were struck by a ransomware attack. The report also found that organizations with more successful responses were more likely to have the following in their ransomware response plan:
- backup verifications and frequencies
- backup copies and assured cleanliness
- containment or an isolation plan
- alternative infrastructure arrangements
- a pre-defined chain of command
As organizations look to adopt more cyber-resilient data protection strategies, Veeam continues to form strong partnerships with hardware and cloud vendors, making it easier to adopt immutable backup repositories, air-gap solutions, or (as the best practice) both.
Our software offers immutability with Microsoft Azure, Direct to S3 with Immutability, and enhanced tape backups, and Veeam Data Cloud Vault helping organizations improve the efficiency of their backups and better defend themselves against the impact of ransomware infections.
Veeam Data Cloud Vault offers seamless integration within the Veeam ecosystem, providing Veeam Data Platform users with an accessible and secure immutable storage solution.
See the power of Veeam for yourself by watching our detailed backup demos. Alternatively, subscribe to our Product News newsletter below to get more updates about our backup and recovery solutions, or contact us to learn how you can partner with Veeam.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What are air-gap backups?
Air-gap backups are copies of your data that are completely isolated from any network. They can be physically disconnected or digitally segregated. This means attackers can’t remotely access, encrypt, or delete them, making air gap backups a reliable last line of defense against ransomware and other cyber threats. - How do immutable backups differ from traditional backups?
Immutable backups are designed so that, once written, the data can’t be modified or deleted for a set period. Unlike traditional backups, which could be altered if a system is compromised, immutability locks the data down. It gives you a clean, untouchable recovery point even if ransomware strikes. - What is the 3-2-1-1-0 backup rule?
- It’s a modern backup best practice:
- 3 copies of your data
- Stored on 2 different types of media
- 1 copy kept off-site
- 1 copy that’s air-gapped or immutable
- 0 errors — meaning your backups are regularly tested and verified for integrity.
With this approach you get maximum protection and recoverability, no matter what disaster comes your way.
- How can combining air gap and immutable backups improve cyber resilience?
Combining both gives you layered protection: immutability keeps data safe from tampering even when online, while air gap backups ensure there’s a physically isolated copy that’s unreachable by attackers. Together, they significantly increase your odds of recovery after a cyberattack. - What are the cost implications of using these backup strategies?
Costs can vary based on the technologies used. Air gap backups may involve physical storage like tapes or offline disks, which come with handling and storage expenses. Immutable backups typically involve cloud storage or specialized hardware, which may scale with data volume. However, the cost of not having these protections, such as ransom payments, data loss, and downtime, is far greater. It’s an investment in business continuity. - How can Veeam assist in managing backup storage effectively?
Veeam provides a unified platform that simplifies backup storage across on-prem, cloud, and hybrid environments. With features like backup immutability, in-line malware scanning, and Veeam Data Cloud Vault, you can automate retention policies, control storage costs, and secure your data — all from one interface. - What compliance benefits do immutable backups offer?
Immutable backups help organizations meet data retention and integrity requirements mandated by regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and SOX. By preventing data tampering and ensuring an unalterable audit trail, immutability supports compliance with security and privacy standards, reducing regulatory risk. - How do air gap backups fit into a broader enterprise data strategy?
Air gap backups play a critical role in an enterprise’s cyber resilience and disaster recovery plan. By providing an offline, untouchable recovery option, they complement cloud and on-prem solutions. For organizations handling sensitive or regulated data, adding air gap storage strengthens protection against cyberattacks and natural disasters.
More resources:
- https://www.veeam.com/resources/wp-veeam-data-cloud-vault-v2.html
- https://www.veeam.com/resources/videos/webinar-ransomware-trends-report-2025.html
- https://www.veeam.com/resource/video/cyber-resiliency.html