Key Takeaways:
- Layer your defenses, don’t rely on one tool or feature. Combine zero-trust principles, immutable backups, and threat detection to stop attacks before they spread.
- Backups are your non-negotiable safety net. Store at least one immutable, air-gapped copy and test restores regularly so you can recover cleanly without paying ransom.
- Know how attackers move. Identify MITRE ATT&CK TTPs to spot and block phishing, credential theft, lateral movement among many other tactics ransomware groups rely on.
- Detect threats early. AI-powered scanning, IOC tools detection, and behavioral-based monitoring can reveal threat actors activity before encryption starts.
- Practice recovery like it’s game day. Orchestrated cleanroom recovery testing and automated playbooks reduce downtime and mistakes when every minute counts.
How can organizations prevent ransomware with today’s advanced and sophisticated threat landscape? It starts with building a strategic and layered defense. This includes deploying immutable backups, enforcing zero-trust principles, identifying attack vector and MITRE ATT&CK framework tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTP), and preparing with orchestrated recovery and up to date incident response plans. Ransomware prevention demands technical depth and proactive planning.
In this blog, we’ll break down proven ransomware prevention practices and show how Veeam’s platform can help your organization protect data, detect threats earlier, and stay resilient and ready to recover.
Understanding Ransomware
What is ransomware, and how does it actually impact organizations?
Ransomware is a form of malicious software designed to encrypt an organization’s data and demand payment in exchange for its release. But beyond encryption, modern ransomware campaigns are carefully orchestrated attacks that may include data exfiltration and other forms of extortion. Ransomware attack TTPs are designed to maximize leverage.
Understanding how ransomware works is the first step to stopping it. Today’s threat actors often operate like well-funded businesses, using legitimate tools (like RDP, PowerShell, and AnyDesk) to quietly infiltrate environments, move laterally across systems, disable security controls, and encrypt high-value assets.
While you are focused on building your business, threat actors’ sole job is to find weak points in your network and systems to compromise and exploit them. Organizations that fail to understand how ransomware operates, and adjust their strategies accordingly, face increasing risk of prolonged downtime and business disruption.
The technical anatomy of a ransomware attack typically involves:
- Initial access through phishing, software vulnerabilities, or exposed remote services
- Lateral movement to find weaknesses and identify where to execute an attack
- Data discovery and staging, often targeting file servers and backups
- Execution of encryption and/or exfiltration of sensitive data
- Extortion — often involving dual threats of data loss and public leaks
The consequences go far beyond lost files. A successful ransomware attack can:
- Paralyze operations for days or weeks
- Expose sensitive or regulated data
- Trigger compliance violations and breach notifications
- Damage customer trust and brand reputation
- Incur massive recovery costs, often far beyond the ransom itself
That’s why prevention and rapid recovery are strategic parts of your incident response and business continuity plans.
How Ransomware Enters
Recent high-profile campaigns (e.g., associated with Qilin, Interlock, and BlackCat/Crux) exploited newly disclosed vulnerabilities, like Fortinet CVEs from 2024, to gain entry via exposed firewalls, VPNs, or misconfigured remote services. Attackers also used phishing and sophisticated social engineering, such as impersonating share‑point or help‑desk staff, or deploying cloned IT support pages, to bypass MFA and convince employees to install backdoors.
In practice, ransomware entry channels are many and include:
- Phishing and BEC (business email compromise): Targeting email users, to steal credentials and/or install malware.
- Stolen credentials or purchased access: Often traded through Initial Access Brokers on the dark web.
- Unpatched vulnerabilities: In VPN, firewall, systems, applications, APIs, or file transfer services like MOVEit.
- Remote Desktop or administrative tools: With social engineering access via remote tools such as exposed RDP ports, AnyDesk, TeamViewer, or PuTTY.
Top TTPs & Ransomware Behavior
| MITRE Category | Common Techniques & Tools | Typical Use |
| Initial Access | Phishing (MITRE ID# T1566), Exploits (T1190) | Entry via email or vulnerability |
| Execution | PowerShell (T1059.001), cmd.exe | Run scripts or payloads |
| Persistence | Scheduled Tasks, Registry Autostart (T1547) | Maintain access |
| Credential Access | Mimikatz, LSASS dumping (T1003), keyloggers | Steal admin credentials |
| Discovery | Network scanning, AD queries (T1087, T1018) | Explore environment |
| Lateral Movement | RDP, PsExec, WMI, AnyDesk (T1021) | Spread to other hosts |
| Defense Evasion | Shadow copy deletion, AV disabling (T1562) | Avoid detection |
| Exfiltration | RClone, WinSCP, FTP (T1041, T1567) | Extract data before encryption |
| Impact | File encryption, data corruption (T1486) | Lock files, demand ransom |
Knowing how threat actors get in and move laterally helps your security team deploy layered defenses:
- Enforce least privilege user access and MFA to reduce credential misuse.
- Monitor remote access tools and scripts for abnormal behavior.
- Test incident response and cleanroom recovery workflows using real-world TTP simulations.
- Embed MITRE ATT&CK TTP mapping into key security controls, detection rules, and response playbooks.
The Crucial Role of Ransomware Prevention: Why Prevention is Now a Boardroom-level Priority
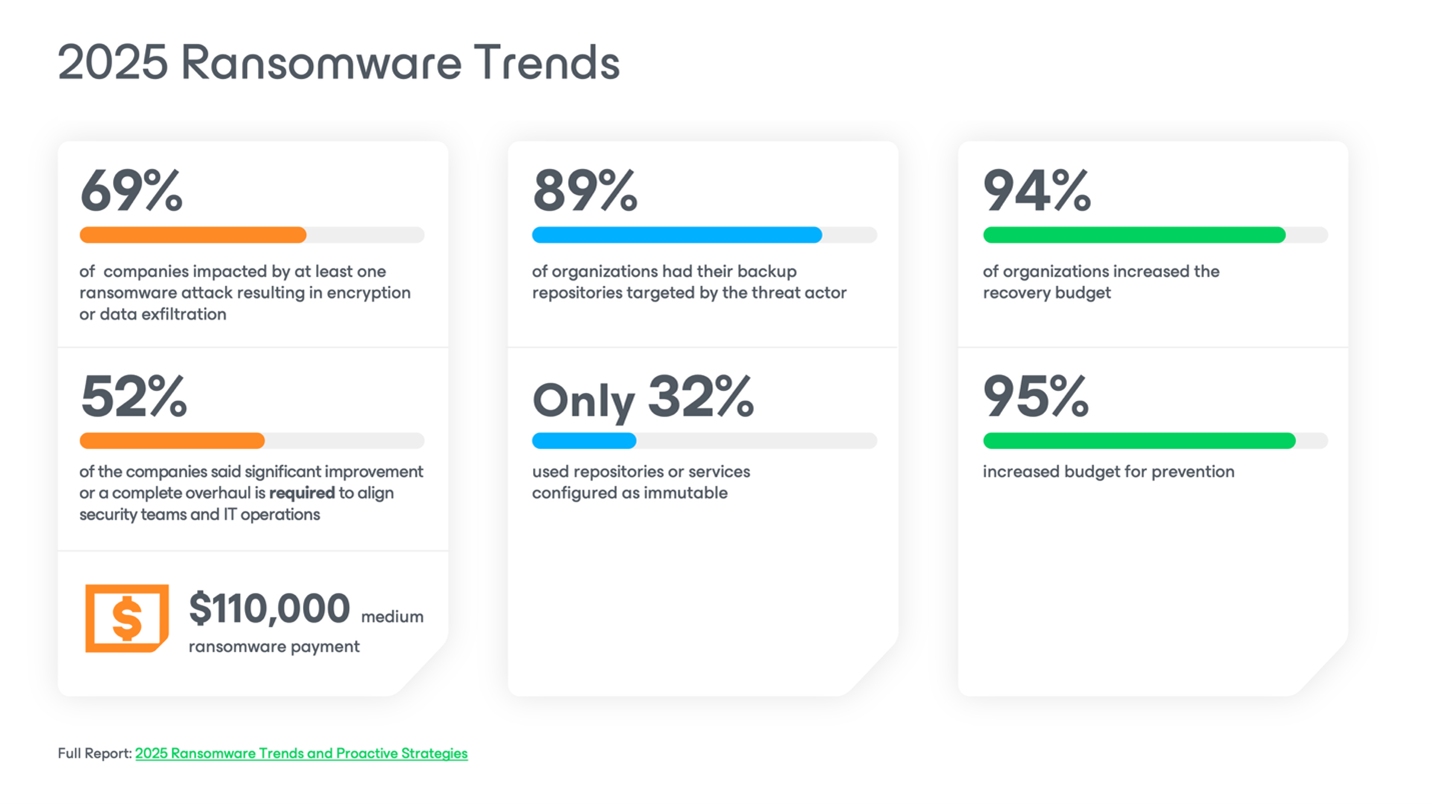
According to the 2025 Veeam Ransomware Trends Report, 94% of organizations attacked by ransomware are increasing their budgets for prevention and recovery. Nearly all acknowledge that recovery readiness is now core to business continuity. And with average cost of a ransomware attack hovering in the millions of dollars, reactive recovery without prevention is a gamble few organizations can afford.
Ransomware prevention should be focused on both stopping malware entry and structuring defenses so that even while systems are compromised, you are able to detect threats before an attack (dwell time) or limit lateral movement, and facilitate containment while preserving clean recovery paths.
Key strategic ransomware prevention priorities include:
- Immutable and encrypted backups: the last line of defense against encryption or deletion by attackers.
- Zero trust access controls: enforcing MFA, least privilege, and segmentation across production and backup environments.
- Signature-based detection: using AI-powered inline scanning, malware detection, and YARA rules.
- Behavior-base detection: to identify suspicious activity in your environments such as potential brute force attacks.
- MITRE ATT&CK TTP alignment: mapping technical controls and detection logic to known adversary behavior to fill security gaps.
- Regular testing & cleanroom verification: validating recovery workflows with orchestration tools and runbooks before you need them.
There is no foolproof way to prevent your business from getting attacked, but a comprehensive cyber resilience strategy can reduce the effects of these attacks and improve the likelihood of recovering your sensitive information.
Building a Strong Ransomware Prevention Strategy: A Multi-Layered Approach
Effective ransomware prevention requires a multi-layered proactive defense strategy designed to block entry, detect threats early, and ensure clean recovery. Here’s how to build one:
1. Prevent Initial Access: Harden the Front Door
- Secure remote access: Disable unused RDP or VPN access, mandate multi-factor authentication (MFA), and enforce session timeout and logging.
- Phishing resistance: Train all staff using realistic phishing simulations, especially targeting finance and HR roles. Enforce email filtering and blocking of macro-enabled attachments.
- Patch hygiene: Automate patch deployment for critical systems—especially VPN appliances, Active Directory, web servers, and operating systems patching. Critical systems and applications should be patched as soon as possible to address high-severity and critical vulnerabilities (CVEs). Monitor vendor advisories for zero-day exposure and rotate vulnerable assets into safe zones.
By disrupting initial entry, you significantly reduce attacker’s opportunity to infiltrate.
2. Secure Identity and Access Controls
- Least privilege: Limit admin rights even for IT staff and backup operators. Use explicit role-based access control (RBAC) and limit admin account use.
- Secure service accounts: Store backup or encryption keys, service credentials, and cloud resource access in a secure vault with audit trails and MFA gating.
- Network segmentation: Separate backup infrastructure networks from production systems and isolate backup storage to reduce risk from lateral compromise.
3. Harden Backup Architecture with Immutable Storage
- Immutable backups: Use immutable object storage, or the Veeam Data Cloud Vault to store protected backup data.
- Follow the 3‑2‑1‑1‑0 backup rule:
– Three copies,
– Two media types,
– One off-site,
– One immutable/offline/air‑gapped,
– Zero surprises through regular recovery validation. - Diversify backups: Maintain multiple immutable copies across on‑prem, object storage, air-gapped, and even WORM tape for full media-level resilience.
Immutable and diversified backups are your safeguard against destructive or tampering attacks.
4. Monitor Behavior and Detect Early Signs
Catching anomalies early can sharply reduce the impact of an evolving attack.
AI-powered inline scanning during backup: Perform inline entropy analysis detection of ransomware encryption and text artifacts including dark web links and ransom notes.
- IOC tools scanner: Identify tools used by threat actors tools like RClone, WinSCP, or Cobalt Strike.
- Proactive threat detection: Use tools such as Veeam’s Recon Scanner to detect suspicious activity mapped to MITRE ATT&CK framework TTPs to prevent attacks.
- Observability layer: Monitor ESXi, vCenter, SSH sessions, new service installations, PowerShell activity, and abnormal VM behavior before, during, and after backup jobs.
5. Test and Orchestrate Recovery
- Cleanroom recovery validation: Regularly test restore points in isolated environments. Make sure you have clean backups by scanning for malware (Veeam Threat Hunter) and using YARA rules scanning. Veeam Recovery Orchestrator can be used to test and automate.
- Runbook automation: Codify response playbooks into executable flows including failover paths, stakeholder alerts, data validation steps to reduce error and manual delays.
- Tabletop simulations: Conduct scheduled scenarios to exercise Plans A, B, and C under varying threat conditions, training cross-functional teams to collaborate under pressure.
At a Glance: Multi-layered Prevention Stack
Layer | Key Controls |
| Access & Identity | MFA, RBAC, phishing training, patching |
| Infrastructure Protection | Immutable backups, network isolation, least-privileged service accounts |
| Detection & Monitoring | AI scanning, IOC detection, observability on backup and production systems |
| Recovery Readiness | Cleanroom validation, secure restore, automated response orchestration |
More information can be found in CISA.gov’s ransomware guidelines.
The Power of Backups: Data Resilience – Your Ultimate Safety Net
When every other control fails, your backup strategy becomes your ultimate safety net. Resilient backups make it all come together.
Why Backups Matter More Than Ever
Ransomware operators often infiltrate environments silently, targeting backups alongside production systems to eliminate recovery options.
- In 2025, Coveware reported that nearly 98% of ransomware cases involved attackers attempting to corrupt or delete backups to pressure victims into paying.
- In contrast, organizations with immutable backup infrastructure and regularly tested restores saw significantly lower rates of ransom payment and downtime, even when infected.
Put simply: without reliable clean backups, recovery may not be possible, and paying the ransom does not guarantee clean data.
Components of a Resilient Backup Strategy
1. Immutable, Isolated Storage:
Use hardened repositories, immutable cloud targets, and/or WORM media to keep backups safe even if attackers gain high-level access.
2. Backup Diversification:
Apply the 3‑2‑1‑1‑0 rule with three copies, two media types, one offsite, one immutable, and zero surprises through testing.
3. Encrypted Backup Copies:
Ensure backups are encrypted at rest and in transit. Guard encryption keys with strict access controls to make data unreadable if exfiltrated.
4. Recovery Validation:
Use tools like Veeam’s Secure Restore and Recovery Orchestrator to validate restore points via Threat Hunter and YARA scans. Test in isolated clean rooms before returning data to production.
5. Off-site and Air-gapped Redundancy:
Replicate backups to secondary locations, use object storage with immutability policies, and include tape or other air-gapped layers.
How Veeam Enables Data-Resilient Backup Architecture
- Immutable backups capabilities & Veeam Data Cloud Vault: Create storage targets that cannot be altered or deleted, even by administrators.
- Encrypted, end-to-end backups: Protect data confidentiality during transfer and at rest.
- Secure Restore & Threat Hunter: Add threat scanning and signature detection into restore workflows.
- Cleanroom recovery via orchestrated validation: Test restores in a safe sandbox to confirm integrity before reintegration.
Advanced Technical Tips for Ransomware Prevention
1. Deploy Deception Tokens and Honeypots
Modern ransomware actors often scout environments weeks in advance. Deploy deception assets, such as decoy credentials, honey folders, or dummy admin hosts, to detect early stages of reconnaissance or lateral movement. Any interaction flags potential targeting before encryption occurs.
2. Micro‑segmentation to Limit Lateral Movement
Especially in hybrid or cloud environments, micro-segmentation enforces the zero-trust principle of segmentation. Even if attackers gain access, they cannot easily move across segmented zones or reach critical systems. This is now a compliance requirement in industries like healthcare.
3. Control Authorization Sprawl
Unchecked permissions on-prem, cloud, or SaaS platforms can create hidden risks. Implement periodic reviews of service and user permissions, providing access to only those who need it. Excess permissions are feast environments for attackers.
4. Monitor for Emerging Browser-Based Exploits and Fake Updates
Recent threats, such as ClickFix-style browser iframe attacks and deceptive fake update pages, have been used by groups like Interlock to deploy malware inline with routine browsing. Combine DNS filtering with behavioral detection in browsers and script runners.
5. Apply Entropy-Analysis Anomaly Detection
Next-generation detection models analyze file entropy within backups and live data to flag early-stage encryption or obfuscation. These models are evolving rapidly, some delivering 97% detection accuracy across ransomware families, even before payload execution.
6. Plan for IoT and OT Risk
Industrial and IoT systems often run unmanaged legacy software. Attackers are increasingly targeting these environments. Segment ICS/OT from traditional networks and include them in your ransomware simulations and recovery plans.
Backups are your final line of defense. Creating a resilient backup strategy is non-negotiable for your organization’s continuity. Backups preserve integrity when tools fail and protect your ability to rebuild.
With Veeam, teams can build backup strategies that are covertly invisible until you need them and bulletproof when the worst happens.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the most effective strategies to prevent ransomware attacks in 2025?
The most effective ransomware prevention strategies in 2025 include enforcing multifactor authentication (MFA), deploying immutable backups, using micro-segmentation to limit lateral movement, implementing zero-trust principles, access controls, and continuously validating recovery through secure restore and cleanroom testing.
2. How does ransomware typically enter an organization’s environment?
Ransomware attacks commonly start through phishing emails, compromised remote access protocols like RDP, exploit software vulnerabilities, or inject malicious attachments. In 2025, attackers increasingly rely on credential theft and business email compromise (BEC), that bypass traditional security tools.
3. What is the 3-2-1-1-0 rule for ransomware protection?
The 3-2-1-1-0 backup rule means keeping:
- 3 copies of data on
- 2 different media types with
- 1 copy off-site
- 1 copy immutable, offline, or air-gapped and
- 0 backup recovery surprises through testing
This model ensures data is both recoverable and resilient, even during a ransomware attack.
4. What is ransomware dwell time and why is it dangerous?
Ransomware dwell time is the period an attacker compromised and remains undetected in your environment before executing an encryption. Longer dwell times allow attackers to find ways to escalate privileges, disable defenses, and target backups, making detection and containment much harder. Reducing dwell time is critical for minimizing impact.
5. Can ransomware infect backups too?
Yes. Many ransomware strains target backup infrastructure by attempting to delete, encrypt, or exfiltrate backups. This is why it’s critical to use immutable storage, segregated access controls, and malware scanning on restore points to ensure data integrity during recovery.
6. What’s the difference between ransomware detection and ransomware prevention?
Ransomware prevention focuses on stopping attacks before they occur, through access controls, patching, and phishing protection. Detection involves identifying suspicious or malicious activity in progress, such as anomalous file changes, encryption behavior, or known indicators of compromise (IOCs). A strong strategy combines both.
