Key Takeaways
- DevOps is a culture, not just a role. It’s about collaboration, automation, and continuous delivery between development and operations.
- Master the essentials first. Start with Git, scripting, Linux basics, and core DevOps tools like Docker, Kubernetes, and CI/CD pipelines.
- Integrate security early. DevSecOps builds security into every stage of the development lifecycle.
- Learn by doing. Hands-on projects, cloud labs, and open-source contributions accelerate real-world skills.
- Stay adaptable. DevOps evolves fast, so commit to continuous learning to stay relevant.
DevOps isn’t a single tool, a job title, or a magic switch to flip. It’s a mindset, a set of practices, and a blend of skills that bring development and operations together to deliver software faster, more reliably, and more securely.
Over the past decade, DevOps has evolved from a niche concept into a mainstream approach that’s used by organizations of all sizes. While the core definition hasn’t changed much, the landscape around it has. AI‑driven automation, cloud‑native platforms, and DevSecOps have expanded what’s possible and introduced new challenges, especially around security.
If you’re starting from scratch, the journey can feel overwhelming. There’s code to learn, tools to master, and processes to understand. But as our community experts emphasize, the fastest way to learn DevOps is to get hands‑on. Build small projects. Experiment with Linux. Contribute to open source. Use cloud-free tiers. The fundamentals you develop now will carry you through any role in the DevOps ecosystem.
This guide distills the essentials into a clear learning path — from foundational skills to modern trends — so you can start building your DevOps expertise today, even if you don’t have “DevOps Engineer” in your job title yet.
What is DevOps?
DevOps is often misunderstood as a tool you buy, a single platform you learn, or a role you apply for. In reality, it’s a collaborative approach to building and running software.
At its core, DevOps brings development (Dev) and operations (Ops) teams together, breaking down silos so software can be delivered faster, more reliably, and more securely. It creates a culture where automation, continuous improvement, and shared responsibility are the norm.
DevOps is a combination of:
- Practices that streamline software delivery and operations.
- Processes that ensure quality, security, and stability.
- Tools that automate repetitive tasks and make workflows more efficient.
- Culture that encourages collaboration across roles and disciplines.
Why the DevOps Definition Hasn’t Changed
The biggest misconception is thinking DevOps is “one big thing”, but it’s actually a collection of skills and methods. The fundamentals are the same as they were years ago, but the ecosystem has evolved:
- AI‑driven automation helps teams code, test, and deploy faster. It also introduces security risks if you don’t understand the generated code.
- Cloud‑native platforms like Kubernetes are now central to many DevOps workflows.
- DevSecOps has emerged, which embeds security practices into every stage of development and delivery.
Think of DevOps as the Evolution of the Sysadmin
A decade ago, system administrators kept servers running, patched operating systems, and managed infrastructure manually. Today’s DevOps engineers do much of the same, with modern automation, orchestration, and code‑driven approaches. The job title may be different, but the goal is the same: Keep systems healthy and deliver value to users.
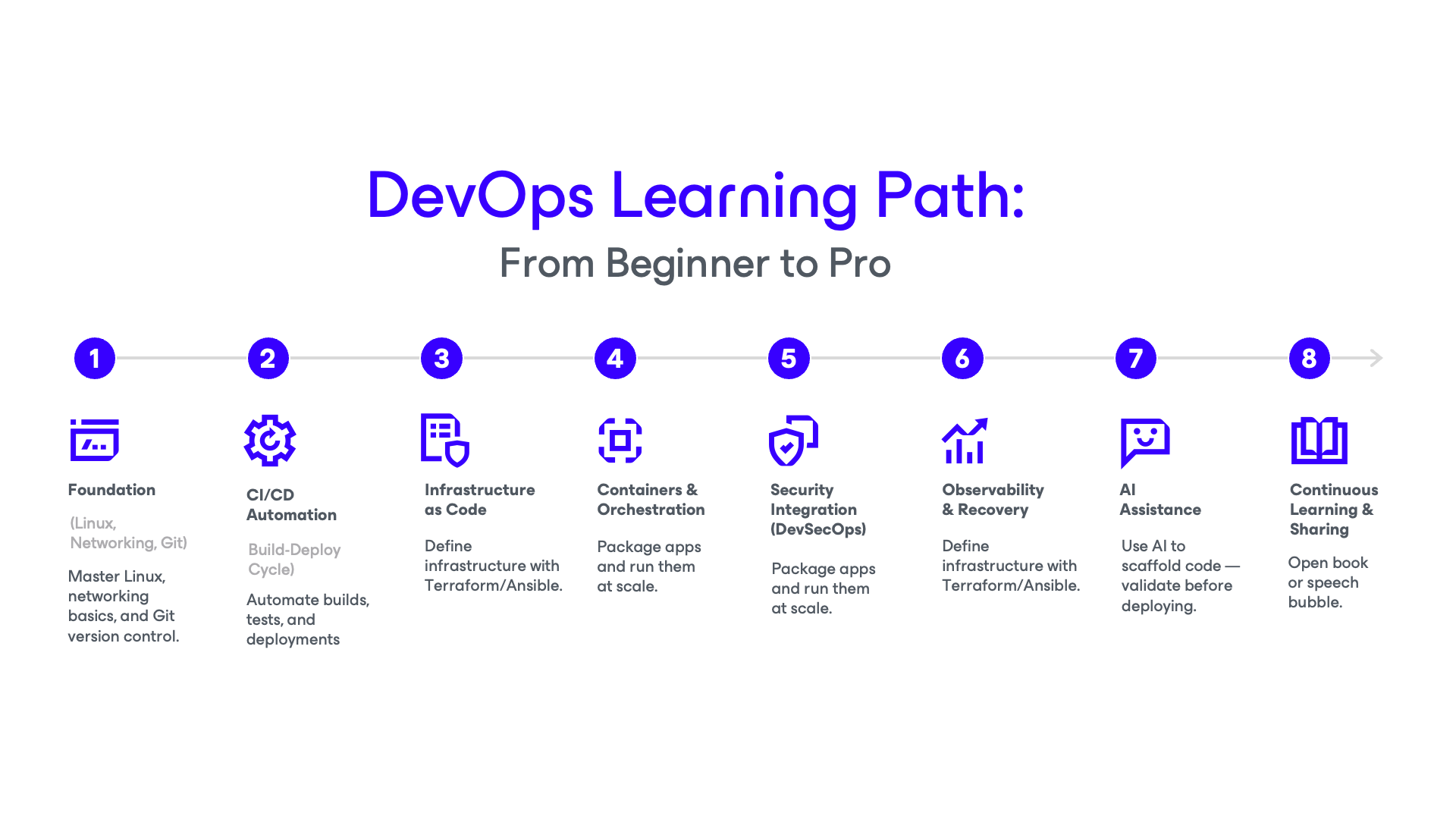
How to Start Learning DevOps
Starting your DevOps journey can feel overwhelming. There’s a huge ecosystem of tools, practices, and concepts to learn. The key is to build a solid foundation before diving into more advanced topics.
1. Begin with Linux Fundamentals
Start with Linux
Linux is open‑source, free, and the backbone of most cloud‑native and DevOps environments. Learning how to navigate the command line, understand file systems, manage permissions, and configure networking will give you skills that transfer to almost every DevOps role.
Practical tips:
- Install a Linux distribution (e.g., Ubuntu, Fedora, Debian) on a spare machine or virtual machine (VM).
- Use free cloud platforms (e.g., AWS Free Tier, Azure for Students, Google Cloud Free Tier) to spin up Linux instances.
- Practice basic commands (e.g., ls, cd, grep, chmod, systemctl) until they become second nature.
2. Get Hands‑On with Real Projects
Reading about DevOps is useful, but hands‑on experience is where skills stick.
Even if you’re not in a DevOps role, you can experiment by:
- Setting up a home lab with VMs or containers.
- Contributing to open‑source projects on GitHub.
- Following guided exercises like 90 Days of DevOps repository.
- Building scenario‑based projects: Deploy a web app, automate backups, configure a CI/CD pipeline, etc.
Pro tip: Document your projects publicly (e.g., on GitHub README, blog posts, LinkedIn). This reinforces your learning while also helping you build a portfolio to show future employers.
3. Learn the DevOps Toolchain
DevOps isn’t about mastering one tool; it’s about knowing how tools fit together in a workflow.
Start with:
- Version control: Git and GitHub/GitLab for managing code.
- CI/CD: Jenkins, GitHub Actions, and GitLab CI for automated builds and deployments.
- Infrastructure as Code (IaC): Use Terraform and Ansible for defining and managing infrastructure.
- Containers and Orchestration: Docker for packaging applications and Kubernetes for running them at scale.
- Monitoring and Logging: Leverage Prometheus, Grafana, and ELK Stack for visibility into your systems.
4. Use AI Wisely
AI can accelerate your learning, but it’s not a substitute for understanding.
Tools like ChatGPT or GitHub Copilot can generate scripts, Terraform configurations, or CI/CD pipelines.
Always review and validate AI‑generated code for correctness and security risks. Combining AI speed with human oversight is the safest way to integrate it into your workflow.
5. Make Security Part of the Process
Security should never be an afterthought; it’s part of modern DevOps (DevSecOps).
Embed security practices early by:
- Using secure coding standards.
- Applying role‑based access control (RBAC) in systems like Kubernetes.
- Keeping dependencies up to date.
- Automating vulnerability scanning in your CI/CD pipeline.
6. Practice Portability and Recovery
Treat every project as if it might need to be moved or restored.
Practice:
- Deploying applications to multiple environments.
- Backing up and restoring data.
- Documenting configuration so anyone can rebuild your setup.
Essential Skills for Modern DevOps
DevOps success comes from combining technical know‑how with a collaborative mindset. While the toolset is vast, the skills will all build on each other, starting from the basics and evolving into advanced automation and orchestration.
Let’s walk through the capabilities that form the backbone of a modern DevOps engineer.
Master Linux First
Linux is the operating system of choice for servers, containers, and most cloud instances. Understanding how to navigate the command line, manage files and permissions, and configure networking is the foundation that everything else rests on. If you can confidently work in Linux, you’ll be comfortable in almost any DevOps environment.
Understand How Systems Talk
Networking fundamentals, such as DNS, TCP/IP, HTTP/HTTPS, firewalls, and routing, are essential for troubleshooting and optimizing deployments. Many production issues boil down to connectivity problems. Knowing how systems communicate helps you diagnose and fix these issues quickly.
Work in Version Control Every Day
Git is more than a code storage tool, it’s the heartbeat of collaboration. Branching strategies, pull requests, and commit history keep teams aligned and enable automation in CI/CD pipelines. If you’re not using Git daily, you’re missing the central nervous system of DevOps workflows.
Automate the Build‑Deploy Cycle
Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery (CI/CD) pipelines take code from commit to production with minimal manual intervention. Tools like Jenkins, GitHub Actions, and GitLab CI let you automate builds, run tests, and deploy applications quickly and reliably. Once you build your first pipeline, you’ll never want to go back to manual releases.
Define Infrastructure in Code
Infrastructure as Code (IaC) allows you to describe servers, networks, and services in configuration files and deploy them consistently across environments. Tools like Terraform and Ansible turn infrastructure into something you can version, review, and replicate. It’s the difference between “it works on my machine” and “it works everywhere.”
Package and Orchestrate Applications
Containers, built with Docker, let you run applications consistently across machines. Kubernetes takes it further, orchestrating containers at scale and handling scheduling, scaling, and failover. In 2025, Kubernetes literacy is a core competency for DevOps engineers.
See What’s Happening in Your Systems
Observability tools like Prometheus, Grafana, and the ELK Stack give you visibility into metrics, logs, and alerts. Instead of reacting to outages, you can detect issues early and respond proactively. In a DevOps role, observability is your radar. Without it, you’re flying blind.
Embed Security from the Start
DevSecOps means building security into every stage of development and deployment. Apply RBAC, scan for vulnerabilities automatically, and protect secrets with tools like Veeam Vault. Security should be woven into the DevOps process.
Collaborate Like It’s Your Job (Because it is)
DevOps is a team sport. You’ll work closely with developers, testers, and operations staff in agile cycles, stand‑ups, and retrospectives. Communication skills, empathy, and adaptability are just as important as technical expertise.
Pro Tip: Build your skills in layers; start with Linux, Git, and CI/CD, then add IaC, containers, and cloud knowledge. Keep security in mind from day one and remember: Hands‑on practice turns theory into skill.
The Role of AI in DevOps: Opportunities and Risks
AI has become a powerful ally for DevOps teams, offering speed and efficiency that were unimaginable just a few years ago. But as with any powerful tool, it must be used with care.
As of 2025, AI can generate Terraform scripts, write CI/CD pipelines, suggest Kubernetes configurations, and even identify performance bottlenecks. For newcomers, it can accelerate the learning curve by pointing directly to relevant documentation, tutorials, and example code.
Where AI Helps
Imagine you need to define infrastructure for a new application using Terraform. Instead of writing every line from scratch, you could prompt an AI tool to scaffold the configuration for you. Or maybe you’re building a CI/CD pipeline; AI can suggest the steps, syntax, and integrations based on your requirements.
AI also shines in learning scenarios. Need a quick refresher on Linux networking commands or Kubernetes RBAC policies? AI can deliver concise explanations and link to deeper resources, saving you hours of search time.
Where AI Can Hurt
Speed comes with risk. If you don’t understand the code AI generates, you might be deploying insecure configurations, introducing vulnerabilities, or creating technical debt. AI can inject “bad things” into your environment if used without review, especially in security‑sensitive areas.
For example, an AI‑generated Kubernetes configuration might grant overly broad permissions (i.e., “God mode”) without you realizing it. Or an automated deployment script might omit critical security checks because the AI model wasn’t trained on your specific compliance requirements.
Best Practices for Safe AI Use in DevOps
- Review everything: Never deploy AI‑generated code without reading and understanding it.
- Validate against known standards: Compare AI suggestions to trusted documentation or security baselines.
- Use AI for scaffolding, not for finished products: Let it handle the boilerplate, then refine manually.
- Combine AI with testing: Ensure automated pipelines include security scans and functional tests before changes hit production.
AI can be a force multiplier in DevOps, accelerating tasks, improving learning, and streamlining workflows. However, it’s not a replacement for human oversight. Treat AI like a junior teammate: Fast, eager, and capable, but in need of review before anything goes live.
Common Pitfalls for Beginners (and How to Avoid Them)
Learning DevOps can be exciting, but it’s easy to fall into traps that slow your progress or create bad habits. Here are some of the most common mistakes beginners make, and how to steer clear of them.
1. Focusing on Tools Instead of Workflows
It’s tempting to dive into Kubernetes or Terraform right away, but without understanding why you’re using them, you’ll end up with fragmented knowledge.
Avoid it: Start with fundamentals like Linux, networking, and Git. Learn how workflows connect before adding complex tools.
2. Ignoring Security
Many beginners treat security as something to “add later.” In DevOps, security must be embedded from the start. Otherwise, you risk building unsafe systems.
Avoid it: Learn basic security practices early, such as RBAC, secret management, vulnerability scanning, and integrate them into your workflows.
3. Blindly Trusting AI‑Generated Code
AI can speed things up, but if you don’t understand the code it produces, you could be deploying insecure or broken configurations.
Avoid it: Use AI for scaffolding, then review and test code before deployment. If you can’t explain what it does, don’t push it to production.
4. Skipping Hands‑On Practice
Reading blogs and watching videos is useful, but until you run commands, deploy applications, and troubleshoot issues yourself, you’re not really learning.
Avoid it: Build labs, deploy sample projects, and break things on purpose to learn how to fix them.
5. Neglecting Documentation
Beginners often skip documenting what they’ve done, which makes it harder to recreate setups or share knowledge later.
Avoid it: Keep notes, write READMEs, and update configurations with comments. Good documentation is part of professional DevOps work.
6. Trying to Learn Everything at Once
DevOps covers a massive range of skills. Trying to master them all at the same time leads to burnout and shallow knowledge.
Avoid it: Follow a learning path; start with Linux, Git, CI/CD, then move to IaC, containers, and cloud. Build depth before breadth.
DevOps is a marathon, not a sprint. Avoid shortcuts that skip fundamentals and always combine learning with doing. Mistakes will happen, but making them in a safe, hands‑on environment is how you grow.
Pro Tip: Hands‑on, scenario‑based learning is the best way to grow. Don’t forget to build security into everything from the start.
DevOps isn’t something you “arrive at”, it’s a continuous process of learning, experimenting, and improving. The technology will change, the tools will evolve, but the principles stay the same: Automate where you can, collaborate across teams, and always keep security in the picture.
You don’t need permission to start; the platforms, tools, and learning resources are already in your hands. Spin up a Linux box, break something, fix it, and document the process. Jump into open source projects. Ask questions in community forums. Every hands‑on step you take not only builds your skillset, but also makes you part of the DevOps ecosystem.
As you follow this roadmap, remember: It’s not about ticking boxes, it’s about becoming someone who can solve problems, adapt quickly, and deliver value, wherever you work.
Ready to Level Up Your Skills?
Join the Kubernetes Korner group to explore hands‑on labs, best practices, and discussions with engineers running workloads at scale. Bring your questions, share your wins, and learn alongside other practitioners.
Start Learning with Kubernetes Korner