Key Takeaways:
- Immutable backups are critical for ransomware defense: Immutable backups—written in WORM (Write Once, Read Many) storage—cannot be modified, deleted, or encrypted for a defined period.
- Immutable is not just a feature, it’s part of cybersecurity strategy: Recognized by CISA and industry frameworks, immutable backups help organizations recover from ransomware without paying ransom, mitigate insider threats, and comply with regulatory retention requirements .
- Veeam supports multiple immutability options: Whether you’re using hardened Linux repositories, object storage with S3 object locks, tape/WORM storage, or Veeam Data Cloud Vault, Veeam supports immutability natively across these architectures.
- Retention and rollback depend on correct configuration: The immutability period must be configured carefully: too short and you lose rollback capability; too long and storage costs — and restore points — increase. Veeam automatically extends block generation and retention.
- Immutable backups coexist with testing tools like SureBackup: Immutable archives should still undergo backup verification and sandbox recovery testing. Combining immutability with automated validation tools guarantees usability—and catches corrupted backup chains early.
Secure backup is essential for any modern organization—it’s no longer just a nice-to-have, it’s a must. Yet many teams find it more challenging than expected, often due to confusion about how to make backup part of a broader cybersecurity strategy to defend against malicious threats.
In the 2025 Ransomware Trends and Proactive Strategies, 89% of organizations have had their backup repositories targeted by attackers. More organizations are now adopting immutable backups as part of their cyber resilience policies and best practices to help defend against cyber threats.
But what exactly is an immutable backup, and why should your organization rely on this technology?
What Is An Immutable Backup?
Immutable backup is a backup that cannot be modified, deleted, or encrypted for a defined period of time. This measure keeps your data secure and recoverable—even during a ransomware attack. The data in immutable backup is stored in a read-only state to prevent tampering, accidental modifications, or deletion.
The U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) recommends using immutable backups to help mitigate ransomware. In CISA’s Stop Ransomware Guide, it highlights the best practice to manage risks from Ransomware is to maintain offline, encrypted backups of critical data, stressing the importance of implementing an immutable backup into your data security strategy. Though immutability is not explicitly mentioned, having an offline encrypted copy is a type of immutable backup. We will discuss more about the different forms supported below.
Why Are Immutable Backups Important?
Immutable backups are more than a core cybersecurity function—they are essential to protecting high stakes data like Personally Identifiable Information (PII) and ensuring public trust. For example, in critical infrastructure sectors, like drinking water, immutability isn’t simply a technical feature; it is a foundational safeguard for public safety, operational resilience, and the integrity of vital systems. That is why GORI selected Veeam Data Cloud Vault, to have a fully managed and highly cost-effective solution to protect their mission-critical data and keep clean water flowing to the people they serve.
A ransomware attack isn’t the only reason why immutable backups are critical. Beyond protecting against data encryption, immutability plays a vital role in a resilient data protection strategy by preventing data loss from accidental changes or deletions.
A few years ago, a government agency was in the news after deleting a large number of files that affected multiple people outside their organization. After investigation, it was determined that this agency had no backups to recover because the files had expired or been deleted as part of a data cleanup exercise. Unfortunately, this was a highly public data loss event that drew negative publicity nationally and resulted in some individuals losing their jobs.
Many other companies have suffered similar data loss events, whether accidental or malicious. They just haven’t been publicized or reported.
Effective backup and immutability strategies compel stakeholders to define clear business service level agreements, helping them strike the right balance between data storage costs and data availability to protect critical information.
Immutable Backup vs. Traditional (i.e., Mutable) Backups
| Feature / Aspect | Traditional (mutable) backups | Immutable Backups |
| Data protection | Backups can be modified, deleted, or encrypted if attacked or misconfigured | Data is write‑once, read‑many (WORM); cannot be altered or deleted until a set retention period elapses. |
| Ransomware defense | Vulnerable—malware can encrypt or destroy backup copies. | Strong safeguard—immutable backups survive ransomware and insider tampering. |
| Data integrity and compliance | Integrity relies on access controls and manual safeguards. | Provides an unalterable audit trail—ideal for regulatory frameworks (HIPAA, GDPR). |
| Storage cost and efficiency | Generally cheaper; easy to delete or overwrite redundant data. | Slightly higher storage cost due to retention rules—but mitigates potential multi-dollar downtime. |
| Flexibility and management | Flexible to update, delete, or prune backups anytime. | Requires careful retention planning; policy defines immutability window. |
| Recovery time objectives (RTO) | Fast restores if data is intact—but reliability depends on backup integrity. | Equally fast, with increased confidence because backups are guaranteed clean. |
| Implementation options | Wide support across on-premises and cloud environments. | Supported via object lock (S3, Azure), hardened repos, or secure snapshots—fully integrated in Veeam. |
| Best use cases | Non-critical data copies, dev/test environments, or cost-sensitive archiving. | Mission-critical systems, compliance-required retention, or ransomware resiliency. |
So, how can you leverage your current backup solution investment and implement immutable backups? Veeam provides several options for implementing immutable strategies and technologies, giving you peace of mind that your data is safe and secure.
With Veeam, it’s possible to use immutable backups in conjunction with traditional methods. While immutable backups may become the default for how most customers store their data, traditional backups can still be used to extend a policy outside the “recoverability zone” or to back up data that isn’t mission critical.
We recommend organizations follow the Veeam’s 3-2-1-1-0 backup rule.
- Three copies of the data
- On two different media
- With one copy being off-site
- And one copy being offline, air-gapped, or immutable
- And zero errors with SureBackup recovery verification
Benefits of Immutable Backups
There are many benefits of immutable backups beyond ransomware resilience, including:
- Data integrity and security
- Data corruption prevention: immutable storage keeps the backup unaltered, protecting against data corruption.
- Protection against cyberattacks: immutable backups can’t be encrypted or deleted by ransomware or malicious insider.
- Compliance with data regulations (HIPAA, SEC Regulations, GDPR,etc.)
- Many regulations effectively require strong data protection measures that immutable
backups provide, even if not named explicitly. For example, GDPR mandates data
integrity and protection against unauthorized changes, which immutability
ensures through temper-proof records and verifiable audit trails.
- Many regulations effectively require strong data protection measures that immutable
- Reliable disaster recovery
- Faster RTOs: having clean backup copies let’s teams restore systems and data immediately.
- Higher RPOs: with an immutable backups system in place, you can back up more frequently and retain restore points securely, which minimizes data loss.
- Preservation of historical data
- Ensuring auditability and compliance: immutable backups form a legally compliant archive of records suitable for audits and long-term data retention requirements.
- Facilitating forensic analysis: unalterable backup serves as a trusted source for breach investigations with clear chain-of-custody and incident root-cause analysis.
- Insider threat protection and human error safeguard: this strategy protects data from accidental deletion or malicious manipulation.
- Cost-effective cyber insurance strategy: while immutability can increase storage needs, it can reduce financial exposure from ransomware demands, downtime, recovery, and even regulatory fines.
Want to see benefits in action? Organizations across the public and private sector are strengthening their data resilience with Veeam. See how businesses like yours benefit from Veeam solutions and turn modern data protection into a strategic business advantage.
Implementing Immutable Backups
The process of implementing immutability depends on your choice of storage technology. But regardless of the technology, the backup strategy should include:
- Following 3-2-1-1-0 backup rule:This builds a foundation for resilient and verifiable backups.
- Choosing an immutable-capable storage backend. The storage needs to support write-once, read-many (WORM) policies.
- Using immutable snapshots and retention locks.
- Using role-based access and privilege separation. This limits who can modify or delete backups and separates duties.
- Implementing offsite copy and delayed deletion.
- Automating backup verification and alerts. Regularly run backup integrity testing and monitor for unexpected deletions or anomalous file activity.
- Testing immutability policies by attempting deletions or modifications of immutable data.
At Veeam, we developed Veeam Data Cloud Vault–a fully managed, secure cloud storage resource fully integrated with Veeam Data Platform, designed to eliminate the complexities of managing infrastructure and unpredictable cloud cost models. Leveraging Microsoft Azure, Veeam Vault offers pre-configured, immutable, and air-gapped storage that is always encrypted, ensuring data security and resilience against cyber threats.
Additionally, Veeam works with over 30 immutable storage partners, giving you unparalleled choice regarding data storage. Let’s examine a typical backup system and look at where you can add immutability and encryption to increase security and resilience.
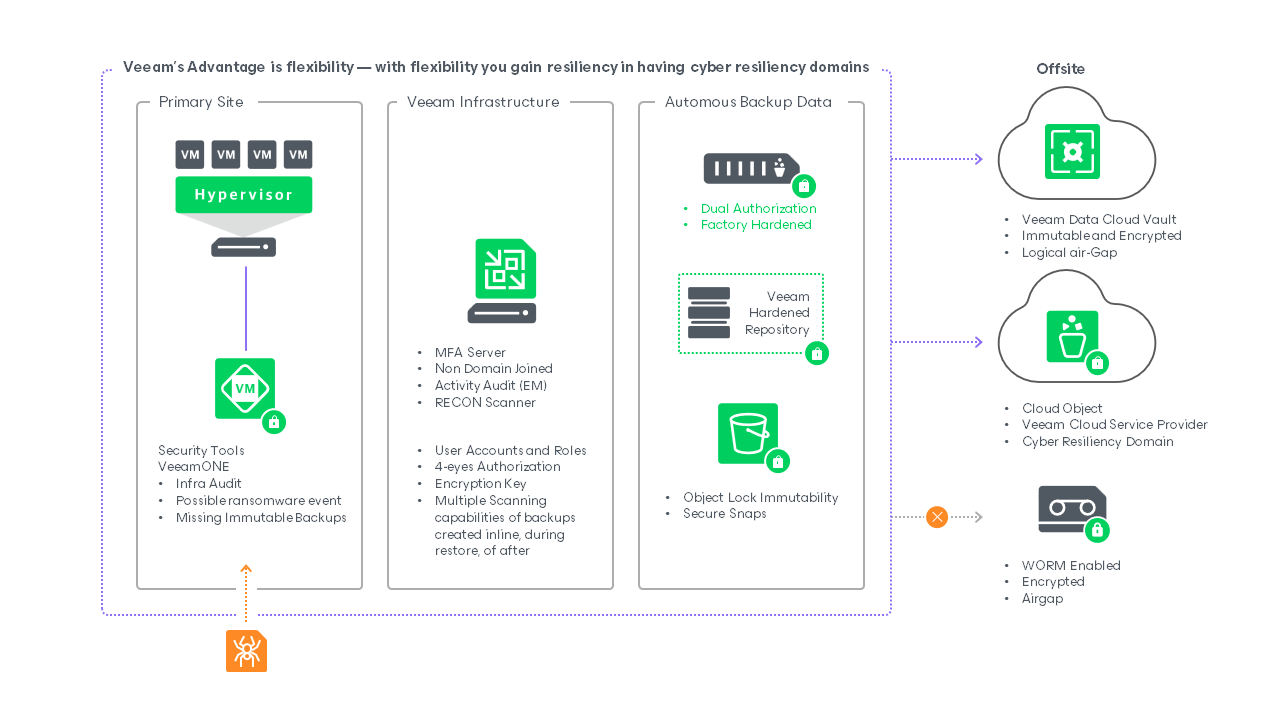
The original data set is found on your production infrastructure. Here, primary storage providers can create immutable (i.e., read-only) volume snapshots of your workloads. This makes it easy to quickly recover from a recent data loss event. Veeam supports taking backups and recovering from storage snapshots to ensure the highest RPOs and RTOs.
Next, we have the Veeam infrastructure with proper access controls. Those controls include multi-factor authentication that is separated from backup storage. If the original data is compromised, changed, or lost, the unaffected backup ensures you have a copy to use for recovery.
Finally, you have an autonomous or isolated clean room with backup data where you have multiple options for storage taking advantage of Veeam backup portability combined with immutability. Let’s break this down further.
How to Implement Immutable Backups with Veeam
| Choose Your Immutable Storage Type | – Hardened Linux Repository: On-premises, using xattr-based immutability on XFS with single-use credentials. – Object Storage with Object Lock/Versioning: S3-compatible services like AWS, Wasabi, IBM Cloud, or Azure Blob. – Managed Cloud Vault: Veeam’s preconfigured secure, air-gapped immutable storage. |
| Configure the Storage for Immutability | For Linux Repository: – Prepare Linux host (install OS, configure XFS, secure SSH). For Object Storage: – Enable object lock and versioning (S3/Wasabi) or WORM (Azure Blob). – Create new bucket or container with these settings. |
| Add the Repository in Veeam Backup & Replication | – Open Veeam Backup & Replication console. – Go to Backup Infrastructure > Backup Repositories > Add Repository. – Select Linux/SMB for Hardened Repo, or Object Storage for cloud targets. – Enable immutability and set retention period (7 to 9,999 days). |
| Set Up Backup or Backup Copy Jobs | Use Backup Copy Jobs or Capacity Tier jobs with immutable targets. – For Linux Repos: Point backup or copy jobs to the hardened repository. – For Object Storage: Use Backup Copy Job directed to the cloud-based immutable repo. |
| Validate and Test Immutability | After backup runs: – Linux: Check for .lock files and _xattr attributes. – Object Storage: Review retention settings in the storage console. – Attempt to delete: Deletion should fail, proving immutability. – Use PowerShell in Veeam to test recovery scenarios. |
| Monitor and Maintain | – Ensure immutability period is longer than job retention. – Check logs, repository settings, and storage object metadata. – Keep Veeam and storage systems updated for full support and security. |
Technology and Infrastructure
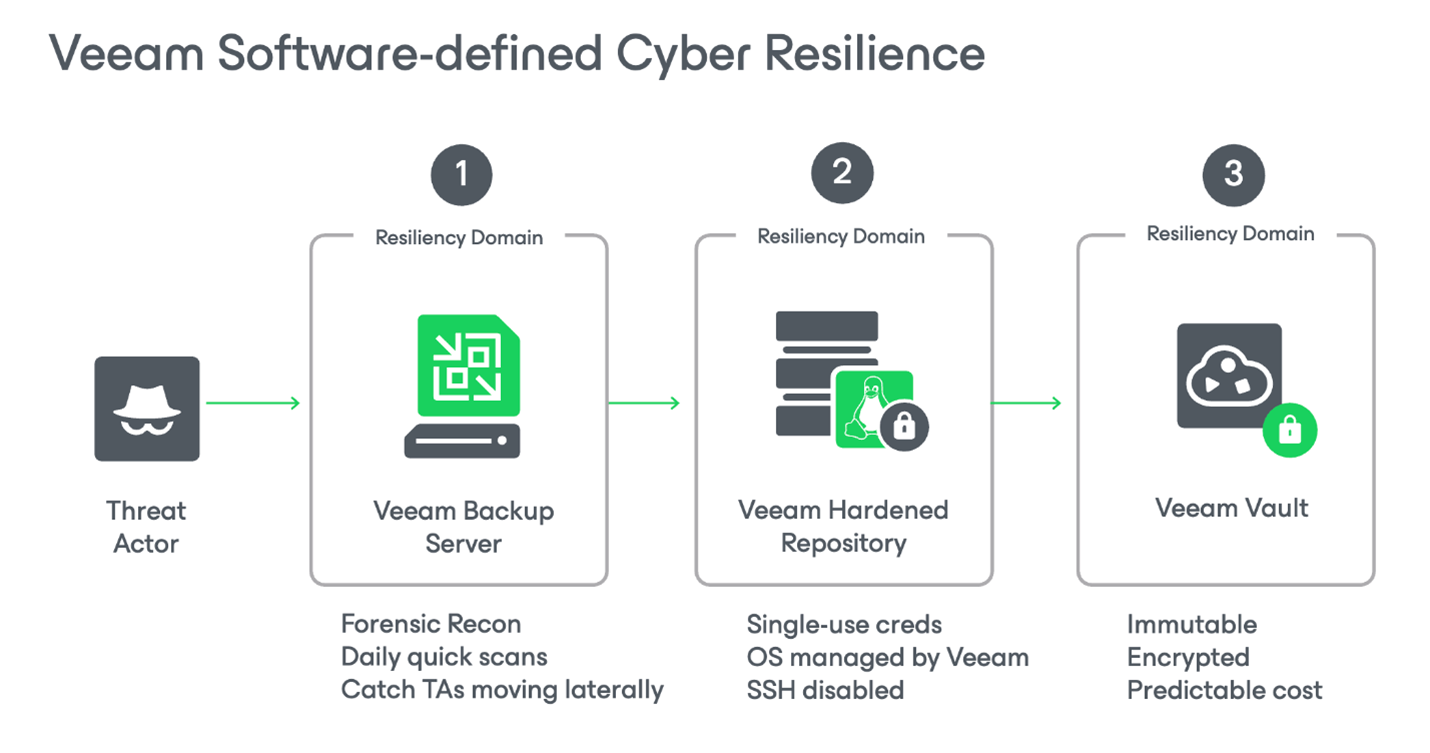
Immutable cloud-based options include the following:
Veeam Data Cloud Vault is always immutable, encrypted, and logically air-gapped from production. This is a great choice for organizations that do not want to invest in additional hardware and overhead for management – Veeam Vault does all this for you in an integrated experience with an immutable policy set by default to 30 days.
Public providers, including AWS and Microsoft Azure, can provide immutability when you create an Amazon S3 bucket or Azure storage.
Other Veeam partners, such as Blackblaze, Wasabi, and 11:11 Systems, provide S3-compatible immutable cloud for Veeam backups.
Ecosystem providers, including IBM and Veeam Cloud & Service Providers (VCSPs), provide immutability on the backend. They can also be used as a Disaster Recovery sites that extend capabilities to replicate the most critical workloads to achieve low RTOs.
Immutable on-premises storage solutions include:
There are over 100 Veeam Ready – Repository partner products which take advantage of Veeam’s deduplication, compression, and XFS Block Cloning, including immutability.
Let’s dive into some of those options below:
Veeam Hardened Repository: This is Veeam’s native solution for storing backups on an immutable disk-based storage server. Server vendors include HPE, Cisco, Dell, Lenovo, and more.
On-premises S3-compatible storage: Featuring object lock immutability with Veeam deduplication and compression, this option includes vendors such as ObjectFirst, Cloudian, DataCore, Dell, ExaGrid, Fujitsu, Scality, IBM, MinIO, Hitachi, SpectraLogic Black Pearl, and many others.
Deduplication appliances: These are disk-based but have deduplication and compression built in. Specifically, HPE StoreOnce have an integration for controlled data immutability (ISV-DI), which requires dual authorization. While others, such as Exagrid, Quantum, Infinidat, leverage time retention locks or secure snapshot technologies for immutability.
Pure Storage FlashBlade//S: This is also an on-premises S3-compatible vendor that leverages object lock immutability and SafeMode Retention Lock as an added layer to protect against insider threats or the compromise of administrator credentials.
Backup Technology Considerations
The vendors listed above have knowledge base articles covering best practices and validated architectures. This lets you adopt an immutable strategy easily. Once immutability is set for certain vendors, it can be difficult to change and sometimes becomes permanent. Therefore, it’s vital to understand your organization’s business SLAs and have agreed-upon retention policies that prevent mishaps for data storage.
Consider the questions below when choosing the best technology for your organization.
- Duration: How fast would you be able to restore your business — 1 day, 1 week, 1 month, or longer? Having multiple recovery strategies is critical to prepare for any data loss event. A traditional snapshot-based backup leaves gaps and risks. Adding at least one immutable backup copy increases your chances of successful data recovery.
- How: Are manual or automated recovery processes in place, and in what order? An outage isn’t the time to determine what workloads to recover first and how long they could take. Having tested and updated documentation for business continuity/disaster recovery is critical, and Veeam can help provide this with Veeam Data Platform Premium Edition.
- Where: Which location have you designated for recovery? Is it the cloud, a service provider, or a second data center? You should consider off-site replication and geographical redundancy when creating a BC/DR plan. If a second site isn’t available, could you leverage a VCSP or a public cloud provider to get data off-site and immutable?
Protect Your Data with Veeam
Veeam is a market leader when it comes to data security, recovery, and flexibility. Veeam Data Platform allows you to prohibit the alteration or deletion of data from backups on different types of backup repositories from hundreds of vendors, with the option to utilize a fully integrated and fully managed secure cloud storage offering.
If you need to secure your data and protect your organization from ransomware and other cyber threats, Veeam’s Backup and Recovery Solutions can help. Get started by downloading a free trial today or explore the Veeam community to get answers to common questions, access free training, and communicate with other users.
If you’re a managed services provider and reseller interested in helping your customers protect their data, partner with Veeam today to deliver data resilience solutions..
Frequently Asked Questions:
- What exactly is an immutable backup?
An immutable backup is a backup copy that cannot be modified or deleted for a predefined retention period—typically stored in write-once, read-many (WORM) storage. It protects against tampering, accidental deletion, and ransomware-encrypted data.
- Why do immutable backups matter now more than ever?
With ransomware and insider threats on the rise, immutable backups ensure you maintain a clean, unaltered copy of your data. Even if production data gets compromised, immutability guarantees recoverable backups.
- How are immutable backups implemented in Veeam?
Veeam supports immutability across several platforms:
– Object storage like AWS S3, Azure Blob, Wasabi with object lock or versioning.
– Hardened Linux repositories with xattr-based file locking.
– Appliances/WORM storage and Veeam-managed cloud vaults.
- What is the immutability period and why does it matter?
The immutability period is how long a backup remains locked and unalterable. Veeam applies this retention across the entire backup chain. It prevents improper deletion—even if a retention policy is changed—until this period expires.
- How do I recover data older than the immutability period or that was deleted?
Veeam includes a PowerShell rollback feature, allowing you to revert object storage to a previous state within the immutable window, even if newer data or changes exist.
- Can immutability overwrite standard retention settings?
Yes. If your immutability window exceeds the backup job retention, Veeam prevents deletion for the immutability period—even beyond the retention policy. This ensures you maintain a complete backup chain.
- What are the minimum and maximum immutability durations?
For hardened Linux repos, Veeam enforces a minimum of 7 days, and supports durations up to 9,999 days—allowing flexible compliance and retention planning.
- How do I test immutability in my environment?
Run a backup to an immutable repository with a short immutability period, then attempt to delete a restore point. Veeam will block the action—proving immutability is working.
