Key Takeaways
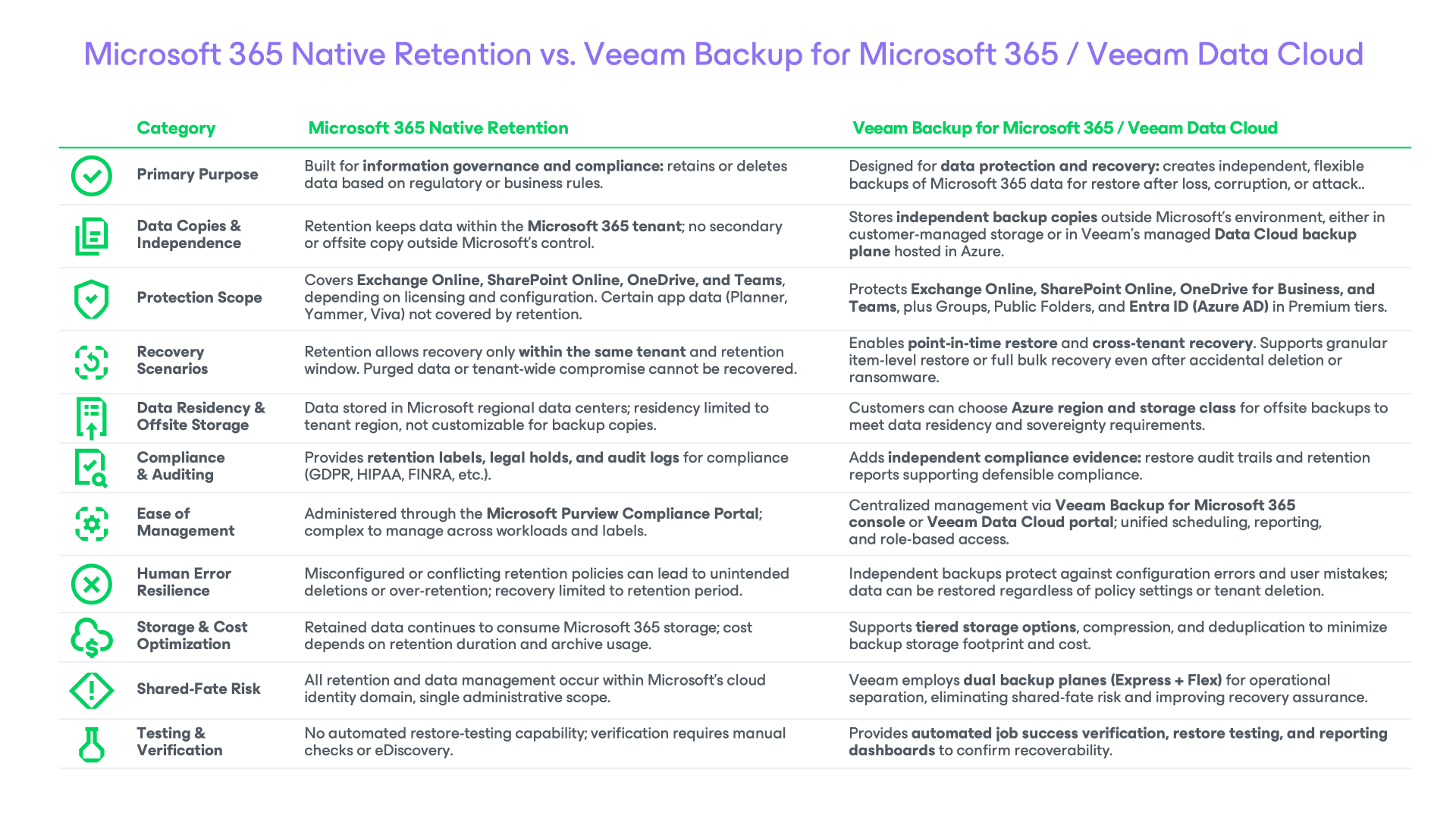
- Data retention is a key compliance and governance tool, but it’s not a replacement for a true backup solution. Retention settings help meet regulatory needs but are often complex and easy to misconfigure. One mistake can cause accidental deletions or policy gaps, so only a dedicated backup can provide full data recovery.
- Align retention with compliance. Use Microsoft 365 retention labels and policies to meet regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and FINRA while avoiding under‑ or over‑retention risks.
- Optimize storage and costs. Automate the deletion of outdated or redundant data across Microsoft Exchange, SharePoint, OneDrive, and Teams to reduce storage bloat.
- Protect sensitive information. Apply retention locks, event‑based retention, and consistent policies to safeguard confidential content during its lifecycle.
- Streamline governance. Standardize retention rules across workloads, regularly review policies, and leverage Microsoft 365’s built‑in automation for efficient data management.
Data retention in Microsoft 365 is the process of preserving, managing, and securely deleting business data, such as emails, documents, and chat messages, while staying in line with regulatory, legal, and operational requirements. It ensures that critical information remains accessible for as long as it’s needed, while removing outdated or redundant data to optimize storage and reduce risk.
In today’s compliance‑driven and security‑sensitive environment, effective data retention is essential for meeting mandates like GDPR, HIPAA, and FINRA, controlling storage costs, and protecting sensitive information. Microsoft 365 provides powerful native tools, including retention labels, retention policies, and eDiscovery, to help organizations automate and enforce governance across Exchange, SharePoint, OneDrive, and Teams.
The Importance of Data Retention in Microsoft 365
In Microsoft 365, retention isn’t only about storage. It’s about meeting legal obligations, maintaining operational efficiency, and safeguarding information throughout its lifecycle.
Compliance
Data retention in Microsoft 365 is essential for meeting legal and regulatory requirements that dictate how long organizations must preserve certain types of data. Failure to comply can result in severe financial penalties and reputational damage.
Microsoft 365 enables you to configure retention policies to preserve data as required by:
- GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation): Mandates that personal data be kept only as long as necessary for the purposes for which it was collected.
- HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act): Requires healthcare organizations to retain medical records for a minimum of six years and ensure their confidentiality and integrity.
- FINRA (Financial Industry Regulatory Authority): Enforces rules for financial services firms to retain business communications for set periods.
By using Microsoft 365’s retention labels and retention policies, you can ensure that required data is preserved for the legally mandated period.
Data Management
Data retention policies in Microsoft 365 help organizations control storage costs, reduce clutter, and maintain access to valuable information.
Retention policies allow you to:
- Automatically delete outdated or redundant data to avoid unnecessary storage consumption.
- Keep critical business information accessible for legal, operational, or historical purposes.
- Apply consistent retention rules across Exchange Online, SharePoint Online, OneDrive for Business, and Microsoft Teams to avoid policy gaps.
By configuring automated retention rules, you streamline data lifecycle management while ensuring that employees can quickly find the information they need without wading through obsolete or irrelevant content.
Security
Data retention in Microsoft 365 also plays a vital role in protecting sensitive information from unauthorized access or data leaks during its lifecycle.
Microsoft 365 security features allow you to:
- Use retention locks to prevent deletion or alteration of protected content, even by administrators.
- Reduce exposure risk by securely deleting data that no longer serves a business or compliance purpose.
- Safeguard confidential content in line with zero trust principles and least privilege access controls.
By combining retention policies with Microsoft 365’s security capabilities, you minimize the attack surface and protect sensitive data for as long as it’s retained and it can be securely destroyed when it’s no longer needed.
To leverage Microsoft 365 for data retention, you must carefully plan and implement policies that balance compliance, management, and security requirements. With effective strategy and guidance, Microsoft 365 provides a range of tools to help organizations meet their data protection obligations in an efficient, streamlined manner. Without the right approach, ineffective policies can lead to non-compliance, runaway storage costs, data loss, and security risks. The key is focusing on your organization’s unique needs and using Microsoft 365’s retention features purposefully and judiciously.
Setting Up Data Retention Policies Across Microsoft 365 Services
To effectively manage data retention in Microsoft 365, you must implement comprehensive policies across all Microsoft 365 services that handle business data. This includes Exchange Online, SharePoint Online, OneDrive for Business, Teams, and any other solutions your organization leverages.
Exchange Online
To set up data retention in Exchange Online, create and apply retention tags and policies that match your compliance and business needs.
Steps:
- In the Exchange Admin Center, create retention tags for mailbox folders, specific emails, or entire mailboxes.
- Define retention periods based on regulatory requirements (e.g., 7 years for financial emails under FINRA).
- Configure actions after the retention period expires, such as moving to an archive mailbox or permanent deletion.
Use a mix of default and personal tags so users can apply retention periods to specific items when needed.
To implement retention in SharePoint and OneDrive, apply site-level or content-level policies to keep or delete information after a set period.
Steps:
- In the SharePoint Admin Center, create site retention policies for documents, lists, libraries, or full site collections.
- Set retention periods by content type or business need (e.g., 3 years for financial reports).
- Enable event-based retention to start the retention clock when a specific event occurs (e.g., contract expiration).
- Apply retention labels to individual documents for more granular control.
Tip: Use retention policies in combination with version history to preserve important document changes while controlling storage growth.
Microsoft Teams
To manage retention in Teams, configure policies for chat messages, channel messages, and shared files.
Steps:
- In the Teams Admin Center, create retention policies for private chats, channel conversations, and file content.
- Set different retention periods for different data types (e.g., 30 days for casual chat, 2 years for project-related channels).
- Ensure policies also apply to Teams files stored in SharePoint and OneDrive.
- Review retention regularly to align with evolving compliance requirements.
Tip: Coordinate Teams retention with SharePoint and OneDrive settings to ensure that both messages and related files follow the same governance rules.
Avoiding Common Data Retention Pitfalls in Microsoft 365
To implement data retention policies effectively in Microsoft 365, organizations must avoid several common pitfalls. Over-retention of data can lead to unnecessary storage costs and difficulty finding relevant information. However, under-retention also risks non-compliance with regulations and loss of critical business data.
Over-Retention: Storing Data Longer Than Needed
It can be tempting to set lengthy retention periods to ensure no data is deleted prematurely. However, this often leads to accumulating excessive amounts of stale data that provides little value. Microsoft 365’s tools like retention labels and policies allow granular control over retention periods for different types of content. Conduct regular reviews of existing policies and make adjustments as needed based on compliance and access requirements.
Under-Retention: Deleting Data Too Quickly
Inadequate retention periods put organizations at risk of deleting data that is still useful or needed for compliance. It is critical to understand regulations like GDPR that apply to your industry and geography. Microsoft 365 retention policies can be configured to automatically retain data as long as mandated by the relevant regulations. It’s also important to enable litigation hold to suspend deletion of content that may be relevant for ongoing legal matters.
Inconsistent Application of Policies
For maximum effectiveness, retention policies in Microsoft 365 must be applied consistently across all relevant services and data types. Exchange Online, SharePoint Online, and Microsoft Teams each provide options to manage retention, but policies should be standardized across services. Include all content types like email, documents, chat messages, and channel conversations. Microsoft 365’s retention policy templates provide a convenient starting point, which can then be customized to your needs.
Be mindful of configuration complexity. Microsoft 365 retention rules are complex, involving multiple settings, scopes, and exceptions. This increases the potential for user error or misconfiguration, such as applying the wrong retention label, omitting a content location, or overlapping policies that conflict. These mistakes can lead to unintended data deletion or over‑retention, both of which pose compliance and operational risks. Without a dedicated backup solution in place, such errors can result in irreversible data loss and costly recovery efforts.
By avoiding these common pitfalls and leveraging Microsoft 365’s built-in tools, you can implement data retention policies that reduce risks, cut costs, and streamline compliance. With a well-designed retention strategy that’s supported by solutions like Veeam Data Cloud Solutions for Microsoft SaaS, you can confidently manage and protect data in the Microsoft cloud.
Leveraging Built-in Microsoft 365 Tools for Data Retention
Microsoft 365 offers several built-in tools to manage data retention policies and simplify compliance. By using these features, organizations can optimize retention practices while avoiding common pitfalls like over-retention and excessive storage costs.
Retention Labels
Retention labels allow you to classify data based on sensitivity and set customized retention periods for each label. You can apply retention labels to Exchange email, SharePoint sites, and Teams messages, then manage all labeled items through a unified policy. Retention labels streamline data governance by automatically retaining or deleting items according to your policies.
Retention policies
Create retention policies in the Microsoft 365 compliance center to manage data retention across services. Policies give you granular control to retain or delete data based on content type, location, age, and other properties. For example, you can create a policy to retain all emails over 10 years old in Exchange, or to delete all files in a SharePoint folder after three months. Retention policies apply to an entire organization but can be targeted to specific locations and content types too.
eDiscovery cases
Conducting an eDiscovery case search in Microsoft 365 allows you to find and preserve data that’s relevant to legal matters or internal investigations. The data returned in an eDiscovery case is retained according to your organization’s policies until you choose to delete the case. You can export case data for review if needed while avoiding over-retention by closing cases once they are no longer required. Using eDiscovery for data retention ensures your information is protected and accessible for as long as necessary.
With these built-in tools, you can implement comprehensive yet targeted data retention policies in Microsoft 365. Retaining data for the appropriate length of time and deleting it when it’s no longer needed is key to optimizing storage, ensuring compliance, and maintaining security.
Strengthen Microsoft 365 Data Retention with Veeam Data Cloud
Implementing effective data retention in Microsoft 365 ensures compliance, optimizes storage, and protects sensitive business information. However, native retention policies alone don’t address every risk, such as accidental deletions, ransomware attacks, or gaps in long‑term backup coverage. User error can lead to data loss issues which backups can also address.
This is where Veeam Data Cloud for Microsoft 365 delivers complete peace of mind. By combining Microsoft 365’s built‑in governance features with Veeam’s secure and automated backup and recovery, you get:
- Flexible backups with customizable retention lengths (as long as “forever”).
- Granular recovery options for emails, documents, and Teams data.
- Protection against accidental deletion, corruption, and malicious attacks.
- Audit‑ready compliance reporting for regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and FINRA.
Don’t leave your Microsoft 365 data vulnerable to gaps in retention or unexpected threats. Pair your policies with Veeam’s Data Cloud’s trusted services to ensure your organization can recover quickly, confidently, and completely.
Download your free guide — Microsoft 365 Backup for Dummies, Veeam Software Special Edition — and learn how to protect your Microsoft 365 data the smart way.
FAQs:
You configure retention policies in the Microsoft 365 Compliance Center and apply them across Exchange, SharePoint, and Teams from one location.
Steps:
- Create retention labels and policies in the compliance center.
- Assign them to mailboxes, sites, and Teams content.
- Automate actions (e.g., retain, delete, or both) based on time or events.
- Use consistent rules for similar data types to simplify governance.
2. How does data retention assist with regulations compliance?
Retention policies ensure data is preserved for the legally required period, helping meet mandates like GDPR (e.g., retain personal data only as long as needed), HIPAA (e.g., retain medical records for at least 6 years), FINRA (e.g., retain broker-dealer records for 3–6 years), and SOX (e.g., retain audit records for 7 years).
3. Do retention policies help protect against insider threats or breaches?
Retention policies are primarily a compliance and governance tool, but they support security investigations by preserving evidence. They also ensure important data (e.g., emails, documents, chat logs) is available for forensic analysis after an incident. While they don’t prevent breaches, retention policies help track activity, verify timelines, and recover critical information post‑incident.
4. Do retention policies replace the need for a backup solution?
No. Retention policies are not a substitute for a full backup solution. As Microsoft MVP, Erica Toelle explains: “It takes time to set up retention policies correctly, and admins can make mistakes just like any other user. There are more than a few examples of data loss having occurred due to user error when configuring retention policies. A third‑party backup tool is like an insurance policy that protects your files, emails, and Microsoft Teams conversations from these types of mistakes.”
