- Veeam Glossary
- What Is Vulnerability Management?
What Is Vulnerability Management?
- What Is Vulnerability Management?
- Traditional VM vs. Risk-Based VM
- Vulnerability Management vs. Vulnerability Assessment
- Why Is Vulnerability Management Important?
- Common Vulnerabilities and How They’re Ranked
- How Does Vulnerability Management Work?
- Vulnerability Management’s Key Components
- Common Challenges in Vulnerability Management
- How Veeam Can Help in Vulnerability Management
Vulnerability management (VM) is the process of identifying and assessing vulnerabilities, reporting on them, and managing or mitigating them. The process covers an organization's endpoints, systems, and workloads. It ensures the organization's systems and data stores are secure.
A vulnerability isn’t the same as a threat or risk:
- Vulnerability: A weakness or flaw in a computer system or network that may be exploited by a cybercriminal.
- Threat: A malicious action taken by a cybercriminal to hack into a system, it could include exploiting vulnerabilities.
- Risk: The likelihood of a breach, compromised system or cyberattack by a threat actor.
Traditional VM vs. Risk-Based VM
The traditional approach to vulnerability management aims to identify and fix every vulnerability. This approach may have been feasible when systems were simpler, but now it's impractical. It requires allocating significant resources, and users risk spending too much time on low-risk fixes while neglecting critical issues.
The risk-based approach prioritizes vulnerabilities in terms of their potential impact and threat to the business. Risk-based VM focuses on the issues that could cause the most damage.
Vulnerability Management vs. Vulnerability Assessment
A vulnerability assessment is a one-off process where the IT team scans the system for vulnerabilities. As part of the assessment, they typically categorize vulnerabilities they’ve discovered regarding their criticality and threat. A vulnerability assessment is the first step of vulnerability management. VM is the ongoing process of identifying, prioritizing, and fixing vulnerabilities based on severity.
Why Is Vulnerability Management Important?
In 2024, more than 40,000 common vulnerabilities and exposures (CVEs) were reported — a 38% increase from the previous year. Vulnerabilities have been identified in all major software platforms and products. VM helps businesses secure software, networks, and endpoints to protect data from ransomware and hackers.
The benefits of VM include:
- Improved security: Effective vulnerability management lowers the risk of compromise.
- Early threat detection: You can detect threats faster, thanks to regular and ongoing vulnerability scanning.
- Lower risk of data exfiltration: Improved compliance with data protection requirements results in a lower risk of data theft.
- Improved system availability: There’s less enforced downtime due to vulnerabilities.
- Greater resilience to cyberattacks: Improved system security reduces the possibility of a successful attack.
- Lower costs: You experience fewer data breaches and a lower risk of fines for data loss or meeting regulatory compliance.
Common Vulnerabilities and How They’re Ranked
Vulnerabilities are rated according to criteria developed by the CVE Program. Cybersecurity vulnerabilities are assigned a CVE ID and stored in a publicly accessible catalog, the NIST National Vulnerability Database (NVD). Vulnerabilities are given an ID that begins with the letters CVE, followed by the year the vulnerability was identified and a unique sequence number. Before publishing in the NVD, CVEs are verified, and the NVD record shows the severity, the versions affected, and whether the vulnerability has been fixed.
Vulnerabilities have two separate risk ratings, which are determined by the Forum of Incident Response and Security Teams (FIRST). The Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) ranks vulnerabilities according to severity based on attack vectors, scope, and impact metrics. See the table below for more info:
| Vulnerability Severity | CVSS Base Score |
|---|---|
| 0 | None |
| 0.1 to 3.9 | Low |
| 4.0 to 6.9 | Medium |
| 7.0 to 8.9 | High |
| 9.0 to 10.0 | Critical |
The second rating is the Exploit Prediction Scoring System (EPSS), which estimates the probability of the vulnerability being exploited as a percentage between zero and 100%.
You can access the CVE records from the CVE details database and search for vulnerabilities according to various criteria. Other sources for this information include the NIST National Vulnerability Database.
Low-severity vulnerabilities may cause an app to crash or reveal relatively innocuous information about the system. They might also require a specific and unusual combination of system settings and installed applications to be exploited. A high or critical vulnerability is likely to affect systems running the software and has more serious consequences if exploited. For example, a remote execution vulnerability that could be exploited to run ransomware would be a critical exploit.
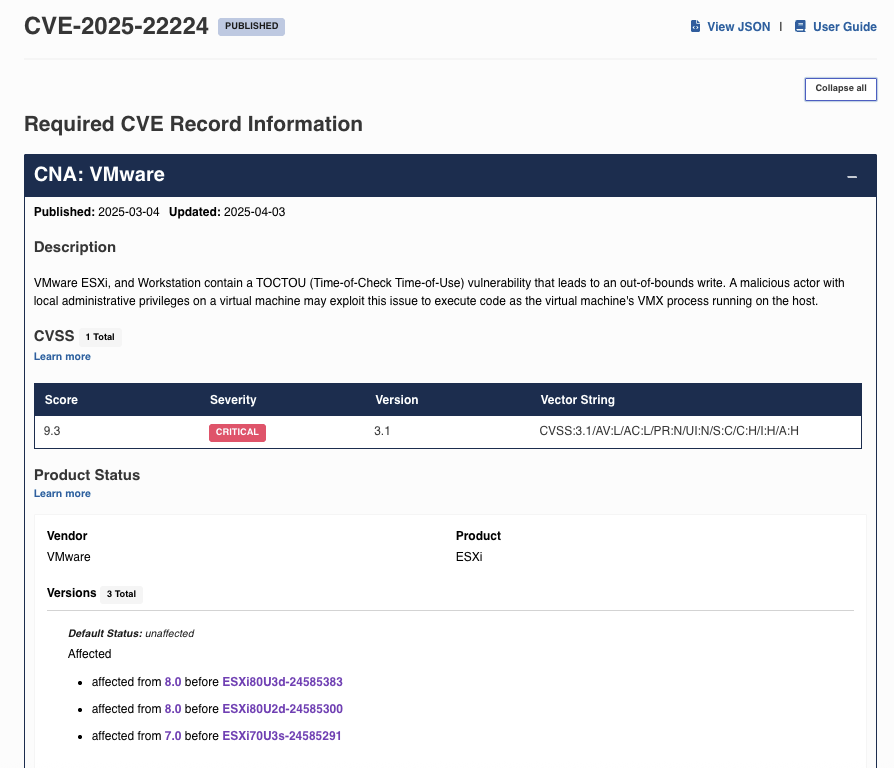
See an example of a critical vulnerability with high CVSS severity:
How Does Vulnerability Management Work?
Vulnerability management is the continuous and often automated process of identifying, assessing, treating (i.e., remediating or mitigating), and reporting on security vulnerabilities in an organization's IT infrastructure, systems, and applications.
Vulnerability management is recommended within the guidelines from the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST). NIST created the Cybersecurity Framework (CSF 2.0), which offers guidance on managing cybersecurity risks.
The published Cybersecurity Framework explains the principles and practices organizations can adopt to manage risk. The ISO/IEC 27005:2022 is another well-established standard for information security, cybersecurity, and privacy protection. While the cybersecurity framework is a guideline, the ISO standard aims to help organizations meet the requirements for ISO 27001 information security, cybersecurity, and privacy protection certification.
Vulnerability Management’s Key Components
A vulnerability management system should include the following components:
Asset Discovery and Inventory
IT management should maintain a comprehensive inventory of all assets, including endpoints and systems. A complete and up-to-date inventory ensures all digital assets are counted and there’s visibility into versions and releases. Inventory scanning tools are also available to identify assets.
Vulnerability Scanning
You should regularly scan systems for vulnerabilities, including the source code and third party and open source libraries. It’s recommended that you use automated tools to regularly scan systems for known vulnerabilities.
Patch Management
Organizations should use patch management software that continually checks for recent updates and patches -- automated patch management is more effective than manual checks. You should apply security and software patches at the earliest opportunity to apply fixes to known CVEs and minimize exposure to vulnerabilities.
Configuration Management
This is about maintaining secure configurations for all systems and tracking changes to ensure compliance with security policy. Organizations should consider using security configuration management software to automate configuration scanning. Properly securing systems and having backups in place to mitigate exploits or prevent ransomware attacks significantly reduces security risks too.
Remediating Vulnerabilities
After identifying vulnerabilities, software development and security teams can consider how they’d be exploited and ensure all avenues are protected. The key to effective remediation is prioritizing based on severity and impact vulnerability fixes (i.e., patches). It's crucial to document all the changes made so you can provide evidence of steps taken to ensure compliance.
Common Challenges in Vulnerability Management
Depending upon where you start, the process of virtual machine (VM) management may be overwhelming, so you might need help getting started with addressing your most critical vulnerabilities. Common challenges and their solutions include the following:
- Resource constraints: If your team is small or inexperienced, consider hiring a managed vulnerability management services team to get started. They can help set up a program and, if required, manage it until the team can take over.
- False positives: Scanners may identify false positives. Reasons may include incomplete information, misconfigured scanning tools, and outdated definitions. Constantly check for the latest definitions and get help from vendors to set up the scanners correctly.
- Rapidly evolving threats: With potentially dozens of vulnerabilities identified, especially in large code bases, scanning tools must have constant automatic updates.
- Incomplete asset inventory: This is a common problem, especially if you're just starting out with vulnerability scanning. Maintain an inventory of all assets and keep it constantly updated and use network inventory scanning tools to ensure the inventory is complete and up to date.
How Veeam Can Help in Vulnerability Management
Vulnerability management systems are essential for a secure network, but in the case of cyberattacks, it’s also important to have a good backup and recovery system. To learn how Veeam Data Platform can help protect your business data, book a demo today or download a trial and test the software yourself!